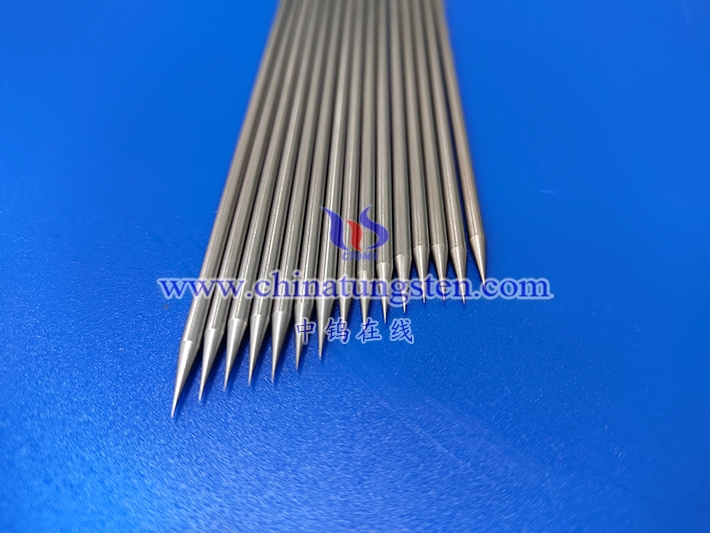
The geometry of tungsten needle tips plays a critical role in producing sharp edges in microfabrication. The sharpness of the tip depends on various factors, such as the angle of the tip, the taper angle, and the tip radius. A smaller tip radius and a steeper taper angle generally result in a sharper needle tip.
Tungsten needles with sharp tips can be used for a wide range of microfabrication applications, such as cutting, drilling, etching, and lithography. These applications require high precision and accuracy, and the sharpness of the needle tip is a critical factor in achieving the desired results.
For example, in lithography, sharp tungsten needle tips are used to create fine patterns on a substrate by selectively removing material. The tip geometry can determine the resolution and quality of the pattern produced.
In summary, the tip geometry of tungsten needles plays an important role in their ability to produce sharp edges in microfabrication applications. A sharper tip can lead to higher precision and accuracy, making tungsten needles with the appropriate geometry highly suitable for various microfabrication techniques.






