Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy Overview
1.1 Definition and Classification of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
1.1.1 Ternary System Composition Range
1.1.2 Density Classification and Application Association
1.2 Development History of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
1.2.1 Origin and Early Research
1.2.2 Military Application Driven Period
1.2.3 Large-Scale Application in Modern Electronics Industry
Chapter 2 Microstructure of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
2.1 Microstructural Characteristics of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
2.1.1 Distribution of Tungsten Particles
2.1.2 Distribution of Ni-Cu Bonding Phase
2.1.3 Sintering Neck Formation Mechanism
2.2 Microstructure and Interface Characteristics of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
2.2.1 Tungsten-Binder Phase Interface Bonding Strength
2.2.2 Effects of Trace Elements on the Interface
2.3 Microstructural Evolution of W-Ni-Cu Alloy
2.3.1 Grain Growth Law during Sintering
2.3.2 Regulation of Microstructure by Heat Treatment
Chapter 3 Physical and Chemical Properties of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
3.1 Mechanical Properties of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
3.1.1 Room Temperature Tensile Strength
3.1.2 Elongation
3.1.3 High Temperature Resistance
3.1.4 Impact Toughness
3.2 Thermal and Electrical Properties of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
3.2.1 Thermal Conductivity
3.2.2 Conductivity
3.2.3 Thermal Expansion Coefficient
3.2.4 Heat Dissipation Performance
3.3 Chemical Stability of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
3.3.1 Corrosion Resistance
3.3.2 Antioxidant Properties
3.4 CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy MSDS
Chapter 4 Performance Testing and Standards of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
4.1 Composition Analysis Method of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
4.1.1 Spectral Analysis Technology
4.1.2 Impurity Element Detection
4.2 Performance Test Method of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
4.2.1 Density and Compactness Test
4.2.2 Tensile Strength and Yield Strength Test
4.2.3 Ductility Test
4.2.4 Toughness Test
4.2.5 Thermal Performance Test
4.2.6 Electrical Performance Test
4.2.7 Chemical Performance Test
4.3 Standard System of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
4.3.1 Chinese National Standard for Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
4.3.2 International Standards for Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloys
4.3.3 Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy Standards in Europe, America, Japan, South Korea and Other Countries around the World
Chapter 5 Preparation Technology of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
5.1 Raw Material Pretreatment
5.1.1 Tungsten Powder Spheroidization and Particle Size Control
5.1.2 Surface Treatment of Nickel-Copper Powder
5.2 Powder Metallurgy Process
5.2.1 Powder Mixing Process Parameters
5.2.2 Pressing Technology
5.2.3 Liquid Phase Sintering Process
5.3 Advanced Preparation Technology
5.3.1 Metal Injection Molding
5.3.2 Hot Isostatic Pressing Technology
5.4 Post-Processing and Processing
5.4.1 Precision Machining
5.4.2 Surface Treatment Process
Chapter 6 Application of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy in Electronic Information Field
6.1 Chip Packaging and Heat Dissipation
6.1.1 High-Power Device Heat Dissipation Substrate
6.1.2 5G RF Module Counterweight Heat Sink
6.2 Microwave and Radar Equipment
6.2.1 Antenna Weight Assembly
6.2.2 Radar Shielding Components
6.3 Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems
6.3.1 Inertial Sensor Counterweight
6.3.2 Micro-Balance Components
Chapter 7 Application of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy in Energy and Industry
7.1 New Energy Vehicle Field
7.1.1 Motor Rotor Weight
7.1.2 Battery Pack Heat Dissipation Substrate
7.2 Industrial Cooling Solutions
7.2.1 Server Cooling Base
7.2.2 Power Semiconductor Packaging Substrate
Chapter 8 Application of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy in the Field of National Defense and Military Industry
8.1 Electronic Countermeasures Equipment
8.1.1 Countermeasures Weight Assembly
8.1.2 Radar Decoy Components
8.2 Ammunition System
8.2.1 Projectile Warhead Counterweight
8.2.2 Missile Warhead Balancing Components
8.3 Armour and Protective Equipment
8.3.1 Lightweight Armour Plate Reinforcements
8.3.2 Armoured Vehicle Protective Linings
8.4 Space Weapons
8.4.1 Rocket Engine Nozzle Components
8.4.2 Spacecraft Attitude Control Counterweights
Chapter 9 Application of Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy in Medical Field
9.1 Radiotherapy Equipment
9.1.1 Radiotherapy Shielding Assembly
9.1.2 Radiation Collimator Components
9.2 Diagnostic Imaging Equipment
9.2.1 CT Detector Protection Parts
9.2.2 MRI Equipment Counterweights
9.3 Surgical Instruments
9.3.1 High-Precision Surgical Navigation Positioning Components
9.3.2 Minimally Invasive Interventional Device Guide Components
9.4 Rehabilitation Assistive Devices
9.4.1 Prosthetic Joint Weight Components
9.4.2 Balance Adjustment Parts for Rehabilitation Equipment
Chapter 10 Comparison between Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy and Other Materials
10.1 Analysis of Competitive Materials of Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy
10.1.1 Comparison with Tungsten-Nickel-Iron Alloy
10.1.2 Comparison with Copper Tungsten Alloy
10.2 Research and Development of Cutting-Edge Technology for Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
10.2.1 Nanostructured Alloys
10.2.2 Functionally Graded Materials
10.3 Green Manufacturing Technology of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
10.3.1 Environmentally Friendly Preparation Process
10.3.2 Waste Recycling Technology
Chapter 11 Common Problems and Solutions of Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy
11.1 Preparation Process of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
11.1.1 Sintering Defect Solutions
11.1.2 Composition Uniformity Control
11.2 Application Failure Analysis of Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
11.2.1 Thermal Cycle Failure Solutions
11.2.2 Environmental Corrosion Protection
Appendix:
Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy Terminology
References
Chapter 1 Overview of Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy
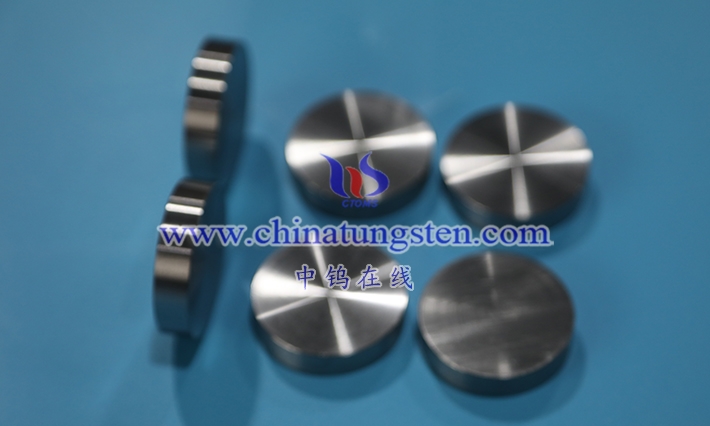
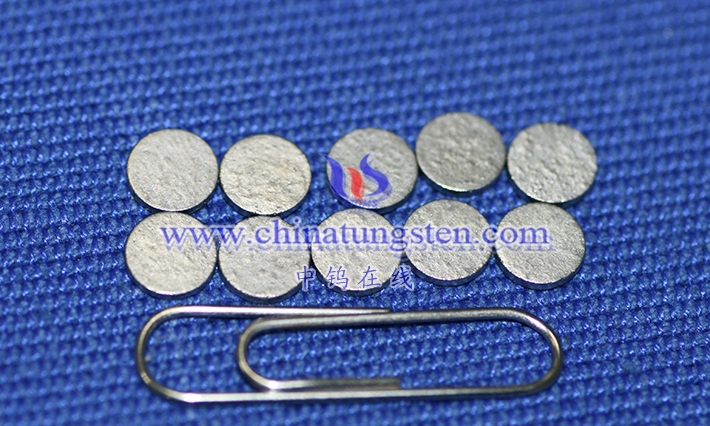
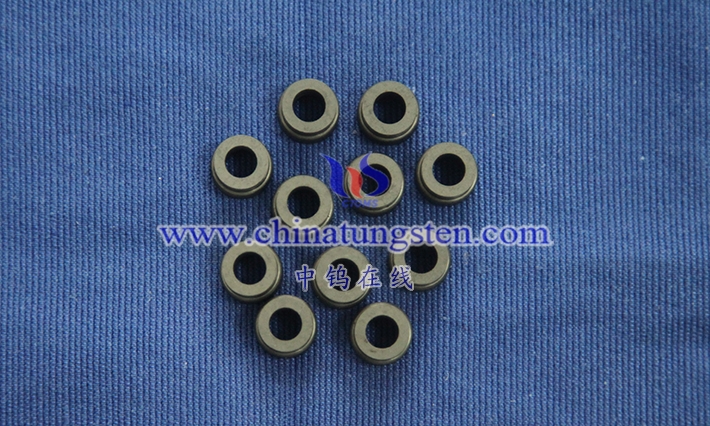
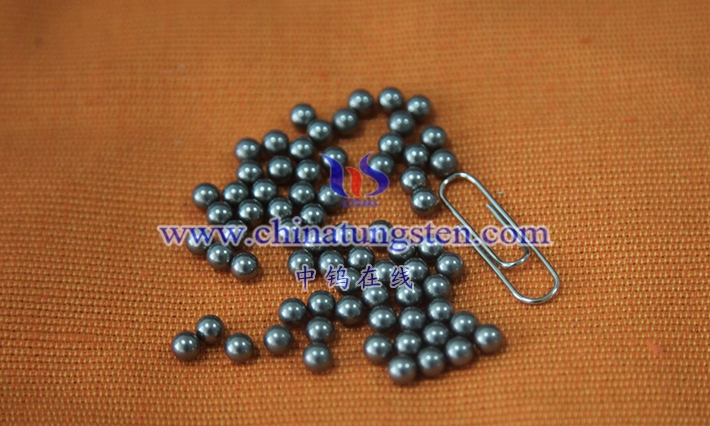
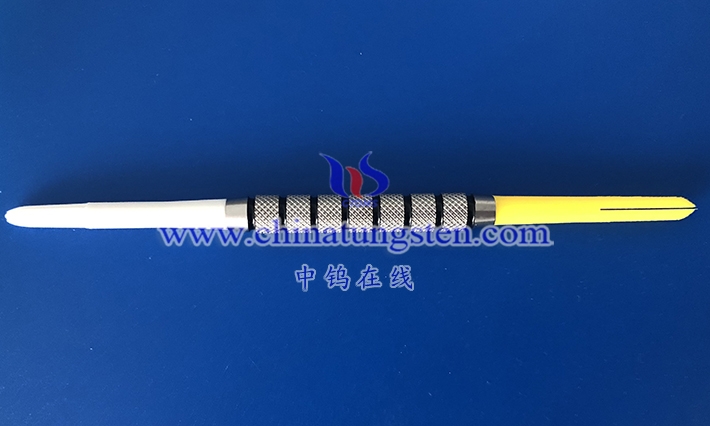
Tungsten -nickel-copper alloy is a high-density alloy with tungsten as the main component and nickel and copper as the bonding phase. It is widely used in aerospace, medical, precision instruments and military industries due to its high density (16.5-18.5 g/cm³), excellent mechanical properties (tensile strength 700-900 MPa, elongation 5%-15%), non-magnetic properties and good corrosion resistance. Compared with tungsten-nickel-iron alloy, tungsten-nickel-copper alloy has non-magnetic properties due to the addition of copper, which makes it perform well in electromagnetic sensitive environments while maintaining high density and machinability.
1.1 Definition and classification of tungsten-nickel-copper alloy
Tungsten -nickel-copper alloy is a high- density tungsten-based alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. It is mainly tungsten (usually 85%-97% by mass), with nickel and copper as bonding phases, giving the alloy high density, high strength and good processing properties. Its main characteristics are non-magneticity, excellent thermal conductivity (120-150 W/ m·K ) and low thermal expansion coefficient (4.5-6.0×10 ⁻⁶ / ° C), which makes it perform well in scenarios requiring high-density counterweights or radiation shielding. Tungsten -nickel-copper alloys can be divided into different types according to tungsten content, nickel-copper ratio and performance requirements, and are usually classified by density or application field. The following will analyze in detail the composition range of its ternary system and the correlation between density classification and application.
1.1.1 Ternary system composition range
Tungsten -nickel-copper alloy is mainly composed of tungsten (W), nickel (Ni) and copper ( Cu). The ratio of the three directly affects the density, mechanical properties and application characteristics of the alloy. Tungsten , as a high-density element (19.25 g/cm³), is the main component of the alloy, usually accounting for 85%-97% of the mass fraction. Nickel and copper, as bonding phases, fill the gaps between tungsten particles, improve the toughness and processing properties of the alloy, and reduce the hardness (Vickers hardness 250-350 HV), making it easier to process than pure tungsten (hardness>400 HV). The typical composition range of tungsten-nickel-copper alloy is: 85%-97% tungsten , 2%-10% nickel, and 1%-8% copper. The specific ratio is adjusted according to application requirements.
In actual production, the tungsten content determines the density and strength of the alloy. For example, 90W-7Ni-3Cu (90% tungsten, 7% nickel, 3% copper) is a common formula with a density of about 17.0 g/cm³ and a tensile strength of about 750-850 MPa, which is suitable for aerospace counterweights. Increasing the tungsten content to 95W-3.5Ni-1.5Cu can reach a density of 18.0 g/cm³ and a strength of 800-900 MPa, which is suitable for medical radiation shielding. The role of nickel is to enhance toughness and corrosion resistance, and its oxidation resistance (forming a NiO protective layer) enables the alloy to perform well in humid or chemical environments. The addition of copper not only further improves toughness, but also makes the alloy non-magnetic (copper is a paramagnetic material), making it superior to tungsten -nickel-iron alloys in electromagnetically sensitive environments (such as MRI equipment) . The thermal conductivity of copper (about 400 W/ m·K ) also improves the thermal conductivity of the alloy, giving it an advantage in scenarios where rapid heat dissipation is required (such as photolithography machine balance blocks).
READ MORE:What Is Tungsten Nickel Copper Alloy
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595