Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Definition of Tungsten Copper Electrode
1.2 Basic Characteristics of Tungsten Copper Electrode
1.3 Development History of Tungsten Copper Electrode
Chapter 2: Material Basics of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
2.1 Characteristics of Tungsten
2.2 Characteristics of Copper
2.3 Tungsten-Copper Composite Mechanism
2.3.1 Physical Compatibility of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
2.3.1.1 Structural Compatibility
2.3.1.2 Thermal Compatibility
2.3.2 Performance Synergy of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
2.3.2.1 Synergy of Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
2.3.2.2 Synergy Between High Temperature Resistance and Structural Stability
2.4 Key Raw Material Requirements for Tungsten Copper Electrodes
2.4.1 Tungsten Powder Requirements
2.4.2 Copper Powder Requirements
2.4.3 Raw Material Pretreatment Standards
Chapter 3: Physical and Chemical Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
3.1 Physical Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
3.1.1 Density of Tungsten Copper Electrode
3.1.1.1 Density Calculation Method
3.1.1.2 Relationship Between Density and Composition
3.1.1.3 Impact of Density on Applications
3.1.2 Thermal Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
3.1.2.1 Thermal Conductivity
3.1.2.2 Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
3.1.2.3 High Temperature Resistance
3.2 Functional Performance of Tungsten Copper Electrode
3.2.1 Conductive Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
3.2.1.1 Conductivity
3.2.1.2 Resistivity
3.2.1.3 Current Carrying Capacity
3.2.2 Arc Erosion Resistance of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
3.2.2.1 Arc Erosion Mechanism
3.2.2.2 Evaluation of Ablation Resistance
3.2.2.3 Factors Affecting Ablation Resistance
3.3 Other Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrode
3.3.1 Hardness of Tungsten Copper Electrode
3.3.2 Strength of Tungsten Copper Electrode
3.3.3 Toughness of Tungsten Copper Electrode
3.3.4 Wear Resistance of Tungsten Copper Electrode
3.3.5 Corrosion Resistance of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
3.3.6 Anti-Welding and Anti-Adhesion Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
3.4 CTIA GROUP LTD Copper Tungsten Electrode MSDS
Chapter 4: Classification of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
4.1 Composition-Ratio Dominant Classification Tungsten Copper Electrode
4.1.1 High Tungsten Content Electrodes (80%-95% Tungsten)
4.1.2 Medium Tungsten Content Electrodes (50%-80% Tungsten)
4.1.3 Low Tungsten Content Electrodes (20%-50% Tungsten)
4.2 Application Scenario-Oriented Classification of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
4.2.1 Electrodes for EDM
4.2.2 Electrodes for High Voltage Electrical Appliances
4.2.3 Electrodes in Welding Field
4.2.4 Special Electrodes for Aerospace and Military Applications
4.3 Classification of Morphological and Structural Characteristics of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
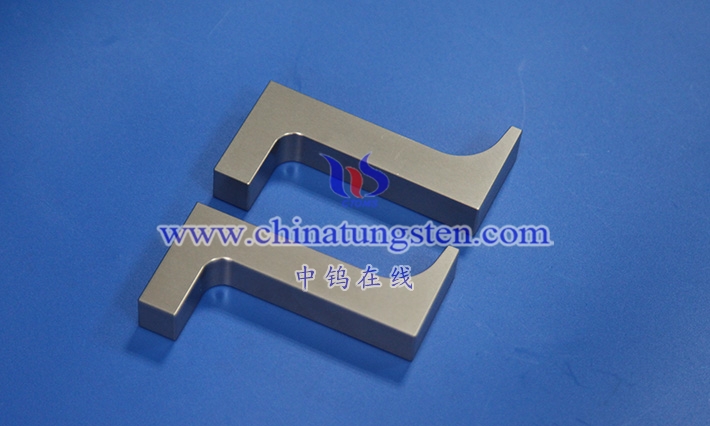
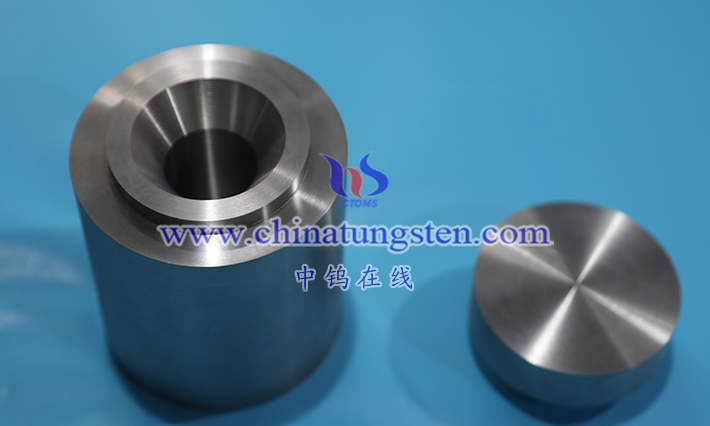
4.3.1 Block Electrodes
4.3.2 Rod Electrode
4.3.3 Sheet Electrode
4.3.4 Special-Shaped Electrodes
4.4 Performance-Driven Classification of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
4.4.1 Highly Conductive Electrodes
4.4.2 Arc Erosion Resistant Electrodes
4.4.3 High-Strength Electrodes
4.4.4 High Heat-Resistant Electrodes
4.5 Classification of Tungsten Copper Electrodes by Microstructure
4.5.1 Uniformly Dispersed Electrodes
4.5.2 Skeleton-Filled Electrodes
4.5.3 Gradient Distribution Electrode
4.6 Classification of Tungsten Copper Electrodes by Macroscopic Physical Form
4.6.1 Dense Electrode
4.6.2 Porous Electrodes
4.6.3 Composite Coating Electrodes
Chapter 5: Preparation Process of Tungsten Copper Electrode
5.1 Infiltration Process
5.1.1 Tungsten Skeleton Prefabrication
5.1.1.1 Tungsten Powder Molding
5.1.1.2 Tungsten Skeleton Sintering
5.1.1.3 Tungsten Skeleton Pore Control
5.1.2 Infiltration Control
5.1.2.1 Copper Material Preparation
5.1.2.2 Infiltration Temperature Control
5.1.2.3 Infiltration Time Control
5.2 Post-Processing Technology
5.2.1 Cutting
5.2.2 Grinding
5.2.3 Surface Treatment
5.2.4 Dimensional Accuracy Control
Chapter 6: Application Scenarios of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
6.1 Application of Tungsten Copper Electrode in EDM
6.1.1 Application in Mold Processing
6.1.2 Application in the Processing of Difficult-to-Process Materials
6.1.3 Advantages of Application in EDM
6.2 Application of Tungsten Copper Electrodes in High Voltage Electrical Appliances
6.2.1 Application in High-Voltage Switches
6.2.2 Application in Lightning Arresters
6.2.3 Application Advantages in High-Voltage Electrical Appliances
6.3 Application of Tungsten Copper Electrodes in Welding and Brazing
6.3.1 Applications in Resistance Welding
6.3.2 Application in Brazing
6.3.3 Application Advantages in Welding Field
6.4 Application of Tungsten Copper Electrodes in Aerospace and Military Industries
6.4.1 Application in Rocket Engine Related Components
6.4.2 Application in Guidance Components
6.4.3 Application Advantages in the Aerospace and Military Industry
Chapter 7: Quality Control and Testing Standards for Tungsten Copper Electrodes
7.1 Detection of Key Indicators of Tungsten Copper Electrode
7.1.1 Physical Properties Test of Tungsten Copper Electrode
7.1.1.1 Density Testing Methods and Standards
7.1.1.2 Thermal Performance Test Methods and Standards
7.1.1.3 Conductivity Testing Methods and Standards
7.1.2 Chemical Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
7.1.2.1 Composition Analysis Method
7.1.2.2 Corrosion Resistance Test Method
7.1.2.3 Impurity Content Testing Standards
7.1.3 Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
7.1.3.1 Hardness Testing Methods and Standards
7.1.3.2 Strength Testing Methods and Standards
7.1.3.3 Toughness Test Methods and Standards
7.2 Microstructure Inspection of Tungsten Copper Electrode
7.2.1 Metallographic Analysis
7.2.1.1 Metallographic Sample Preparation
7.2.1.2 Evaluation Criteria for Phase Distribution Uniformity
7.2.1.3 Grain Size Detection
7.2.2 Defect Detection of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
7.2.2.1 Porosity Detection Method and Permissible Range
7.2.2.2 Crack Detection Methods and Criteria
7.2.2.3 Inclusion Detection Methods and Control Standards
7.3 Industry Standards for Tungsten Copper Electrodes
7.3.1 Relevant Domestic Standards
7.3.1.1 Relevant Provisions of Chinese Standards
7.3.1.2 Industry Standard Requirements
7.3.2 Relevant International Standards
7.3.2.1 International Tungsten Copper Electrode Standards
7.3.2.2 Tungsten Copper Electrode Standards in Europe, America, Japan, South Korea, and Other Countries
Chapter 8: Tungsten Copper Electrode Market and Technology Trends
8.1 Analysis of the Industry Chain of Tungsten Copper Electrodes
8.1.1 Upstream Raw Material Supply
8.1.2 Midstream Manufacturing
8.1.3 Downstream Application Market
8.2 Technical Direction of Tungsten Copper Electrode
8.2.1 Preparation Process Optimization
8.2.2 Performance Improvement Path
8.2.3 Application Expansion Exploration
Appendix:
Tungsten Copper Electrode Glossary
References
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Definition of Tungsten Copper Electrode
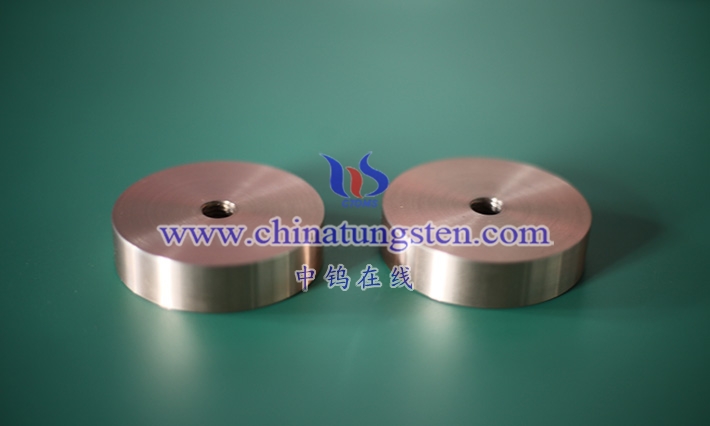
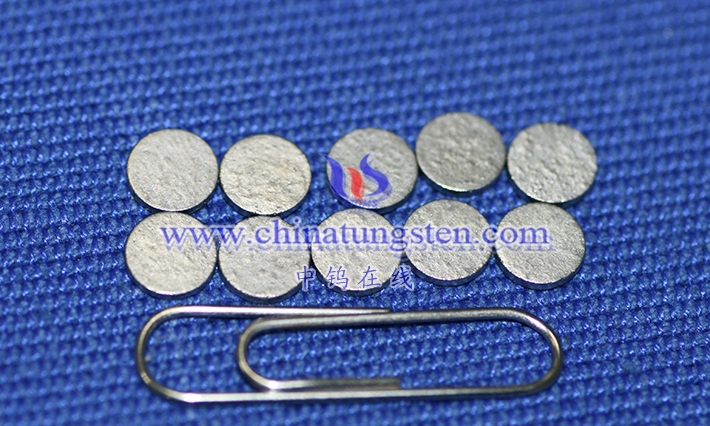
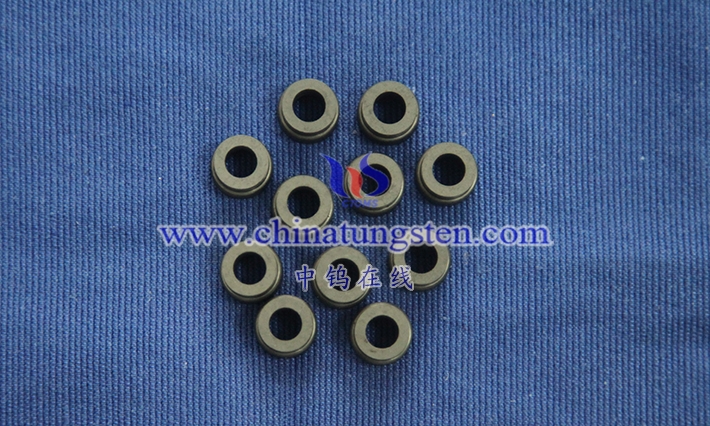
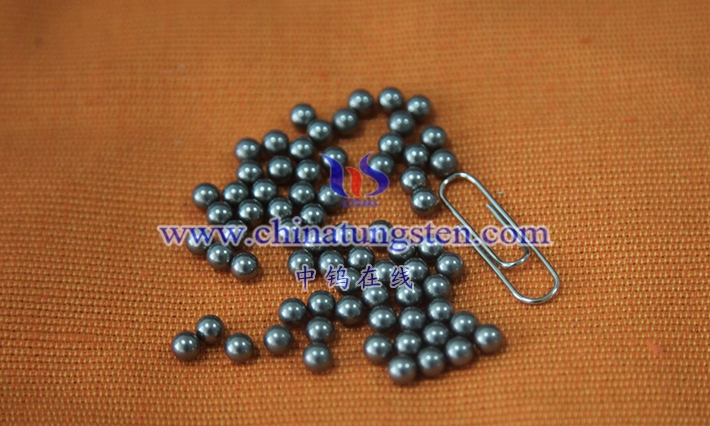
A tungsten-copper electrode is a composite electrode made of tungsten (W) and copper ( Cu) via powder metallurgy or vacuum infiltration. Its definition encompasses its composition, preparation method, and functional properties in specific applications. Tungsten-copper electrodes typically use tungsten as the primary skeleton material and copper as the filler. The two metals are combined in varying proportions (e.g., WCu 70/30, WCu 80/20), resulting in a material with a high melting point, high-temperature resistance, and excellent electrical conductivity. Tungsten’s high melting point of 3422°C gives the electrode exceptional thermal stability and resistance to arc erosion, while copper, with a melting point of 1083°C, possesses high electrical and thermal conductivity, ensuring efficient current transfer and rapid heat dissipation. The properties of this composite material make it widely used in applications such as electrical discharge machining (EDM), resistance welding, and electrical contacts. The definition of a tungsten-copper electrode also encompasses its microstructure. The electrodes are formed by mixing tungsten and copper powders through powder metallurgy, pressing, and sintering, or by infiltrating liquid copper into the porous tungsten skeleton through vacuum infiltration, resulting in a uniform phase distribution and low porosity.
In practical applications, the definition of tungsten-copper electrodes further expands to encompass their functional properties, such as their use as tool electrodes in electrospark machining (EDM) for removing workpiece material, or as electrodes in resistance welding, withstanding high currents and pressures. The ratio and preparation process can be tailored to specific needs. For example, electrodes with a high tungsten content are more suitable for wear and arc resistance, while electrodes with a high copper content optimize electrical conductivity. The definition of tungsten-copper electrodes also encompasses their differences from traditional single-metal electrodes. The advantage of composite materials lies in their balanced properties of tungsten and copper , overcoming the limitations of single materials, such as the low melting point of pure copper or the low electrical conductivity of pure tungsten. In recent years, with advances in manufacturing technology, the definition of tungsten-copper electrodes has gradually expanded to the fields of additive manufacturing and nanotechnology, exploring more refined microstructures and novel applications.
1.2 Basic characteristics of tungsten copper electrode
Tungsten-copper electrodes lie in their unique physical, mechanical, and electrical properties as a composite material, making them particularly suitable for a variety of applications. Firstly, electrical conductivity is a core characteristic of tungsten-copper electrodes . The high electrical conductivity of the copper phase (approximately 5.8×10^7 S/m) provides an efficient current transmission path. Although tungsten has a lower electrical conductivity (approximately 1.8×10^7 S/m), by optimizing the distribution of copper, the electrical conductivity of tungsten-copper electrodes can reach 80%-90% of that of traditional copper electrodes, meeting the requirements of EDM and welding. Thermal conductivity is another key characteristic. The combination of copper’s thermal conductivity and tungsten’s moderate thermal conductivity (approximately 174 W/ m·K ) results in an alloy with a thermal conductivity between 180-220 W/ m·K , enabling rapid dissipation of heat generated during machining or welding, preventing localized overheating.
READ MORE:What Is Tungsten Copper Electrode
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595