Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Basic Knowledge of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
1.1 Tungsten Alloy Disc Performance Advantages
1.1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Disc
1.1.2 Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
1.2 Development History and Technological Evolution of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
1.2.1 Early R&D and Initial Application
1.2.2 Process Breakthroughs and Performance Improvements
1.2.3 Intelligent Production and Diversified Applications
Chapter 2 Classification System of Tungsten Alloy Discs
1.2 Tungsten Alloy Discs by Composition
2.1.1 TungstenNickelIron Alloy Disc
2.1.2 TungstenNickelCopper Alloy Disc
2.1.3 TungstenCopper Alloy Disc
2.1.4 TungstenSilver Alloy Disc
2.2 Tungsten Alloy Discs by Size
2.2.1 MicroDiscs (Diameter < 10 mm) 2.2.2 Conventional Wafers (10 mm ≤ Diameter ≤ 100 mm) 2.2.3 Large Wafers (Diameter > 100 mm)
2.3 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Discs by Application Function
2.3.1 Functional Tungsten Alloy Discs
2.3.1.1 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Radiation Shielding
2.3.1.2 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Electrical Conduction
2.3.1.3 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Thermal Conductivity and Heat Dissipation
2.3.1.4 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Wear and Corrosion Resistance
2.3.2 Structural Tungsten Alloy Discs
2.3.2.1 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Structural Support
2.3.2.2 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Balance Weights
2.3.2.3 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Connection and Fixing
2.3.2.4 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Sealing and Isolation
Chapter 3 Properties of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.1 DensityRelated Properties of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.1.1 Density Range
3.1.2 Density Uniformity Performance
3.1.3 Effect of Density on the Application of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.2 High Temperature Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
3.2.1 Melting Point
3.2.2 Stability in High Temperature Environment
3.2.3 Thermal Shock Resistance
3.3 Surface Properties of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
3.3.1 Surface Roughness Parameters
3.3.2 Flatness Accuracy
3.3.3 Effect of Surface Finish on Use
3.4 Hardness and Wear Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.4.1 Hardness Index Range
3.4.2 Wear Resistance Performance
3.4.3 Relationship Between Hardness and Wear Resistance
3.5 Strength and Toughness of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.5.1 Tensile Strength Value
3.5.2 Bending Strength Performance
3.5.3 Impact Toughness Index
3.5.4 Effect of Strength on the Application of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.5.5 Effect of Toughness on the Application of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.6 Radiation Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.6.1 Shielding Effect Against Gamma Rays
3.6.2 XRay Shielding Capability
3.6.3 Relationship Between Shielding Performance and Thickness
3.6.4 Comparison With Lead Shielding Effectiveness
3.7 Electrical and Thermal Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.7.1 Conductivity Parameters
3.7.2 Thermal Conductivity Range
3.7.3 Correlation Between Electrical Conductivity and Thermal Conductivity
3.7.4 Factors Affecting the Electrical Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.7.5 Factors Affecting Thermal Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Discs
3.8 CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Wafer MSDS
Chapter 4 Performance Test Methods of Tungsten Alloy Discs
4.1 Tungsten Alloy Disc Density Test Method
4.1.1 Density Measurement by Drainage Method
4.1.2 Radiographic Inspection of Density Uniformity
4.1.3 Weighing Method Auxiliary Verification
4.2 Test Method for High Temperature Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Disc
4.2.1 Melting Point Measurement by Differential Thermal Analysis
4.2.2 High Temperature Endurance Strength Test
4.2.3 Thermal Shock Test Method
4.3 Test Method of Tungsten Alloy Disc Surface Properties
4.3.1 Measuring Surface Roughness With a Roughness Meter
4.3.2 Flatness Testing Instrument Operation
4.3.3 Gloss Meter to Measure Surface Finish
4.4 Test Methods for Hardness and Wear Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Discs
4.4.1 Vickers Hardness Tester Hardness Measurement
4.4.2 Wear Resistance Test Using a Wear Tester
4.4.3 Correlation Analysis Test Between Hardness and Wear Resistance
4.5 Test Methods for Strength and Toughness of Tungsten Alloy Discs
4.5.1 Tensile Strength Measurement Using a Universal Testing Machine
4.5.2 ThreePoint Bending Test to Measure Bending Strength
4.5.3 Impact Toughness Testing Machine
4.6 Test Method for Radiation Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Disc
4.6.1 Use of γRay Shielding Effectiveness Detection Device
4.6.2 XRay Attenuation Rate Test Steps
4.6.3 Comparison of Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Discs of Different Thicknesses
4.7 Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Test Methods
4.7.1 Conductivity Measurement Using the FourProbe Method
4.7.2 Thermal Conductivity Measurement Using the Hot Wire Method
4.7.3 Correlation Test Between Electrical Conductivity and Thermal Conductivity
Chapter 5 Production Process of Tungsten Alloy Discs
5.1 Raw Material Selection and Pretreatment of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
5.1.1 Tungsten Powder Purity and Screening
5.1.2 Material Composition Ratio and Mixing
5.2 Forming Process of Tungsten Alloy Disc
5.2.1 Powder Pressing
5.2.2 Sintering Process
5.3 Processing Technology of Tungsten Alloy Wafer
5.3.1 Cutting and Grinding
5.3.2 Surface Treatment
5.4 Quality Control and Inspection of Tungsten Alloy Discs
5.4.1 Online Monitoring of the Molding Process
5.4.2 Random Inspection of All Performance Items of Finished Products
Chapter 6 Application Fields of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
6.1 Application of Tungsten Alloy Discs in Medical Equipment
6.1.1 Radiation Shielding Discs for Radiotherapy Equipment
6.1.1.1 Shielding Applications in Linear Accelerators
6.1.1.2 Local Shielding Design of Gamma Knife Equipment
6.1.1.3 Shielding Layout in Proton Therapy Devices
6.1.2 Counterweight Discs for Medical Imaging Equipment
6.1.2.1 Counterweight Balancing of Rotating Components of CT Machines
6.1.2.2 Stable Counterweights for MRI Equipment
6.1.3 Application of Tungsten Alloy Discs in Nuclear Medicine Equipment
6.1.3.1 Shielding of Radiopharmaceutical Packaging Equipment
6.1.3.2 Protective Components of Radioimmunoassay Instruments
6.2 Application of Tungsten Alloy Discs in Electronics and Semiconductors
6.2.1 Chip Manufacturing Equipment Thermal Conductive Wafers
6.2.1.1 Thermal Conductive Components of Ion Implanters
6.2.1.2 Application of Heat Dissipation Wafers in Photolithography Machines
6.2.2 HighFrequency Device Electrode Wafers
6.2.2.1 Electrode Structure of Microwave Communication Devices
6.2.2.2 Conductive Discs for RF Power Devices
6.2.3 Application of Tungsten Alloy Wafers in Electronic Packaging
6.2.3.1 HighPower Device Packaging Heat Sink
6.2.3.2 Shielding and Packaging of Electronic Components
6.3 Application of Tungsten Alloy Discs in Aerospace
6.3.1 Tungsten Alloy Discs for Spacecraft Attitude Control Weights
6.3.1.1 Satellite Attitude Adjustment Counterweights
6.3.1.2 Balancing Weights for Spacecraft Orbit Change Mechanisms
6.3.2 HighTemperature Resistant Tungsten Alloy Discs for Engine Components
6.3.2.1 HighTemperature Resistant Parts Near Rocket Engine Nozzles
6.3.2.2 HeatResistant Wafers for Space Shuttle Propulsion Systems
Chapter 7 Storage, Transportation and Standards of Tungsten Alloy Discs
7.1 Storage Requirements for Tungsten Alloy Discs
7.1.1 Storage Environment Conditions (Temperature, Humidity, Etc.)
7.1.2 Packaging and Stacking Specifications
7.2 Transportation Requirements for Tungsten Alloy Discs
7.2.1 Transportation Method Selection
7.2.2 Protective Measures During Transportation
7.2.3 Transport Safety Regulations and Labels
7.3 China Tungsten Alloy Disc Standard
7.4 International Tungsten Alloy Disc Standards
7.5 Tungsten Alloy Disc Standards in Europe, America, Japan, South Korea, Etc.
Appendix
Tungsten Alloy Disc Terminology
References
Chapter 1 Basic Knowledge of Tungsten Alloy Wafers
Tungsten alloy discs play a vital role in modern industry and technology. Their unique physical and chemical properties enable them to excel in a wide range of applications, particularly those requiring high density, high temperature resistance, or high strength. The development and application of tungsten alloy discs demonstrates advancements in materials science. Through alloying and precision machining, tungsten alloy discs are able to meet complex requirements while maintaining excellent performance stability.
Tungsten alloy discs are not limited to traditional industrial fields but are also expanding into emerging technologies such as new energy, medical devices, and precision manufacturing. Their versatility and customizability enable them to adapt to the needs of diverse scenarios, making them a key material driving technological advancement. Optimizing the manufacturing process and performance of tungsten alloy discs is a key research area in materials science. Through continuous improvements in alloy formulations and processing techniques, the performance of tungsten alloy discs has been further enhanced, providing a reliable solution for modern industry.
Furthermore, the environmentally friendly nature of tungsten alloy discs makes them crucial for sustainable development. Compared to some traditional high-density materials, tungsten alloy discs are non-toxic, non-radioactive, and recyclable, meeting modern industry’s demand for green materials. This characteristic not only reduces environmental impact but also provides companies with a high-performance material option while meeting environmental regulations. In short, as a versatile, high-performance material, a basic understanding of tungsten alloy discs is crucial for understanding their widespread industrial applications.
1.1 Definition and Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Disc
Tungsten alloy discs are key to understanding their application value. The definition section will explain the material composition, shape characteristics, and manufacturing process of tungsten alloy discs, while the characteristics section will deeply analyze their physical and chemical properties and how these properties give them unique advantages in various scenarios.
1.1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Disc
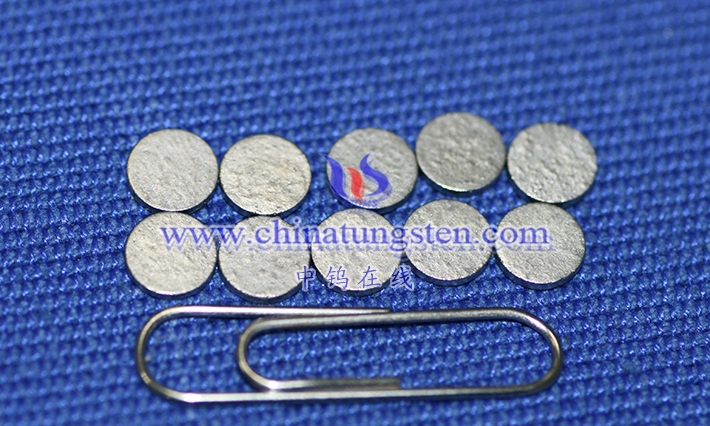
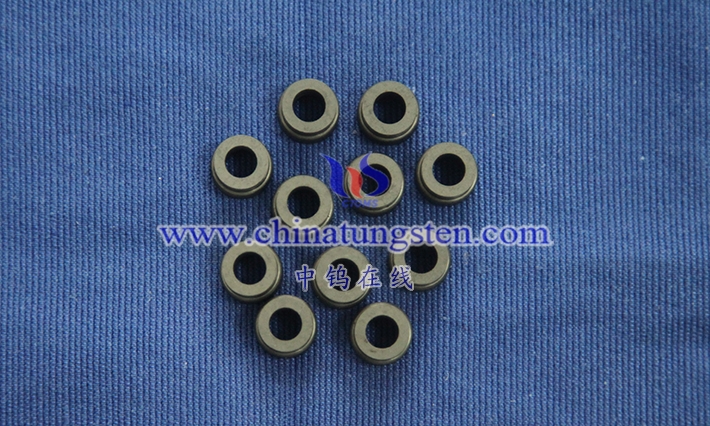
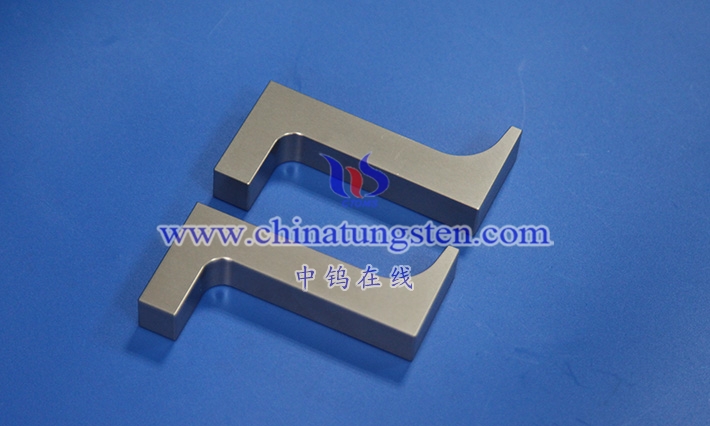
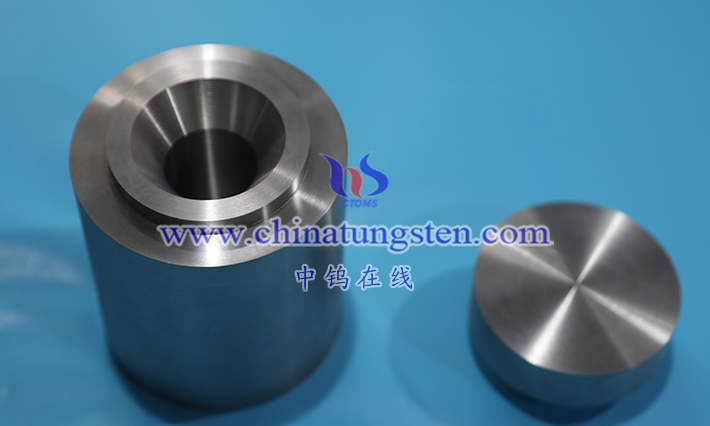
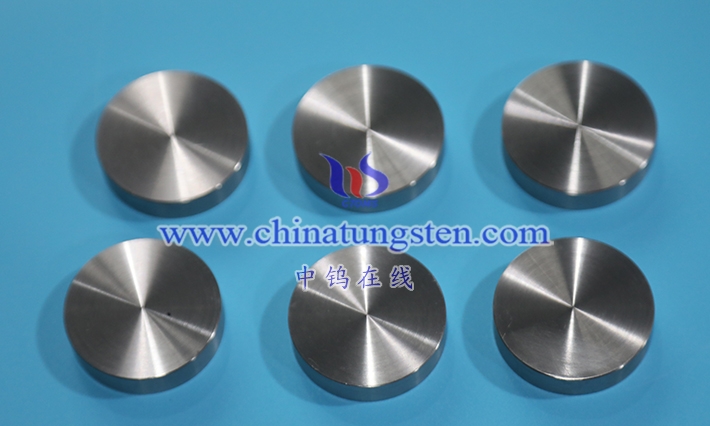
Tungsten alloy wafers are circular, thin sheets primarily composed of tungsten, alloyed with other metal elements (such as nickel, iron, and copper) and processed using a specific process. Their definition extends beyond their circular geometry to encompass their unique physical and chemical properties, giving them broad potential for application in industry and technology. As a high-density, high-melting-point metal, tungsten possesses excellent high-temperature resistance and hardness in its pure form, but its brittleness and processing difficulty also limit its performance. Through alloying, tungsten alloy wafers retain the core advantages of tungsten while significantly improving its toughness and processing properties, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
READ MORE:What Is Tungsten Alloy Wafer
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
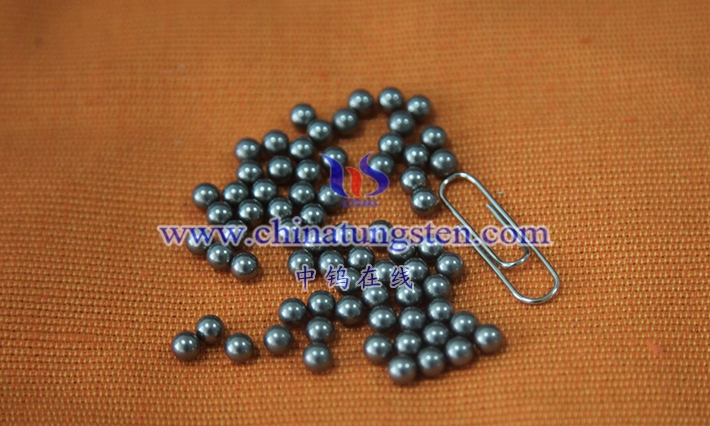
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595