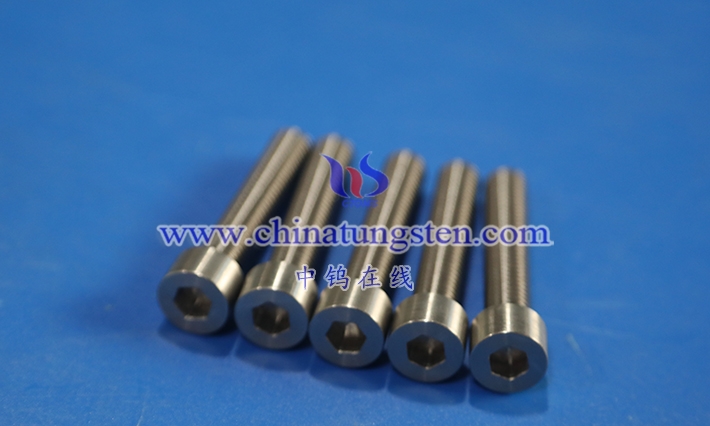
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Definition and Overview of Tungsten Alloy Screws
1.1.1 Concept and Function of Tungsten Alloy Screws
1.1.2 Comparison between Tungsten Alloy Screws and Other Fasteners
1.1.2.1 Performance Comparison with Molybdenum Screws
1.1.2.2 Performance Comparison with Lead Screws
1.1.2.3 Performance Comparison with Steel Screws
1.1.2.4 Performance Comparison with Titanium Screws
1.1.2.5 Differences in Application Scenarios (Aerospace, Medical, Industrial)
1.2 Composition of Tungsten Alloy Screws
1.2.1 Common Components of Tungsten Alloy Screws
1.2.1.1 Tungsten-Nickel-Iron Alloy
1.2.1.2 Tungsten-Copper Alloy
1.2.1.3 Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy
1.2.1.4 Other Tungsten-Based Alloys
1.2.2 Microstructural Analysis of Tungsten Alloy Screws
1.2.2.1 Grain Structure and Phase Distribution
1.2.2.2 Microstructural Characteristics
1.2.2.3 Microscopic Defects and Their Impact on Performance
1.3 Historical Development and Evolution of Tungsten Alloy Screws
1.3.1 Origin of Tungsten Materials in the Fastener Field
1.3.2 Innovation Process of Modern Tungsten Alloy Screws
Chapter 2 Performance and Performance Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1 Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.1 Strength of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.2 Hardness of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.3 Toughness of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.4 Fatigue Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.5 Wear Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.6 Shear Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.7 Creep Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.1.8 Impact Toughness of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2 Functional Properties of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.1 High-Temperature Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.2 Corrosion Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.3 Radiation Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.4 Thermal Expansion Coefficient and Thermal Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.5 Electrical Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.6 Magnetic Properties of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.7 Oxidation Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.2.8 Low-Temperature Brittleness Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.3 MSDS for Tungsten Alloy Screws by CTIA GROUP LTD
2.4 Performance Testing and Evaluation of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.1 Tensile and Compression Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.2 Torque and Shear Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.3 High-Temperature and Low-Temperature Environmental Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.4 Corrosion and Chemical Stability Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.5 Radiation Protection Performance Evaluation of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.6 Fatigue Life and Cycle Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.7 Non-Destructive Testing Methods for Tungsten Alloy Screws
2.4.8 Vibration and Impact Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws
Chapter 3 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.1 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Screws by Function
3.1.1 Standard Fastening Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.1.2 Special-Function Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.1.2.1 Self-Locking Screws
3.1.2.2 Radiation-Resistant Screws
3.1.2.3 High-Temperature Creep-Resistant Screws
3.2 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Screws by Structure
3.2.1 Head Types of Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.2.1.1 Cylindrical Heads and Countersunk Heads
3.2.1.2 Special Head Designs
3.2.2 Thread Types and Geometric Designs of Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.2.2.1 Metric and Imperial Threads
3.2.2.2 High-Strength Thread Optimization
3.3 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Screws by Application Field
3.3.1 Aerospace-Specific Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.3.2 Medical and Biocompatible Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.3.3 Industrial Tungsten Alloy Screws
3.3.4 Military-Grade Tungsten Alloy Screws
Chapter 4 Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Alloy Screws
4.1 Raw Material Preparation and Smelting of Tungsten Alloy Screws
4.1.1 Tungsten Ore Extraction and Powder Preparation
4.1.2 Alloy Smelting Technology
4.2 Forming and Processing Process of Tungsten Alloy Screws
4.2.1 Powder Metallurgy Method and Sintering
4.2.2 Machining and Thread Forming
4.3 Post-Processing and Heat Treatment of Tungsten Alloy Screws
4.3.1 Surface Coating and Passivation
4.3.2 Quality Inspection and Defect Control
Chapter 5 Design and Specification Standards of Tungsten Alloy Screws
5.1 Design Principles of Tungsten Alloy Screws
5.1.1 Geometric Dimensions and Tolerances of Tungsten Alloy Screws
5.1.2 Load Analysis and Stress Distribution of Tungsten Alloy Screws
5.2 International and Industry Standards for Tungsten Alloy Screws
5.2.1 Chinese Standards
5.2.2 International Standards
5.2.3 Tungsten Alloy Screw Standards in Europe, America, Japan, South Korea and Other Countries
5.2.4 Custom Specification Requirements for Tungsten Alloy Screws
Chapter 6 Application Fields of Tungsten Alloy Screws
6.1 Application of Tungsten Alloy Screws in the Aerospace Field
6.1.1 Role of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Engine and High-Temperature Structure Fastening
6.1.2 Mechanism of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Counterweight and Vibration Suppression
6.1.3 Selection Standards of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Aerospace Vehicle Shells and Connectors
6.1.4 Special Requirements of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Satellite Equipment Fasteners
6.2 Application of Tungsten Alloy Screws in the Medical and Radiation Protection Field
6.2.1 Shielding Effectiveness of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Radiation Shielding Equipment
6.2.2 Biocompatibility of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Implantable Medical Device Fastening
6.2.3 Stability of Tungsten Alloy Screws in High-Temperature Sterilization of Medical Equipment
6.2.4 Radiation-Proof Design of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Nuclear Medicine Imaging Equipment
6.3 Application of Tungsten Alloy Screws in the Industrial and Military Fields
6.3.1 Corrosion Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Screws in High-Temperature Furnaces and Chemical Reactors
6.3.2 Strength Standards of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Military Ammunition and Armor Protection
6.3.3 Safety Specifications of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Nuclear Industry and Energy Equipment
6.3.4 Adaptability of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Deep-Sea and Extreme Environment Equipment
6.4 Application of Tungsten Alloy Screws in the Electronic Equipment Field
6.4.1 Miniaturization Design of Tungsten Alloy Screws for High-Density Circuit Board Fixing
6.4.2 Thermal Conductivity Optimization of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Heat Dissipation Modules
6.4.3 Shielding Principle of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Electromagnetic Interference-Resistant Fasteners
6.4.4 Precision Machining of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Micro-Electronic Equipment Connection
6.5 Application of Tungsten Alloy Screws in the Mechanical Manufacturing Field
6.5.1 Load-Bearing Capacity of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Heavy Machinery Structure Fastening
6.5.2 Precision Control of Tungsten Alloy Screws for Precision Mechanical Component Connection
6.5.3 Life Testing of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Wear-Resistant and Vibration-Resistant Mechanical Assemblies
6.5.4 Reliability Requirements of Tungsten Alloy Screws in Automation Equipment and Robots
Chapter 7 Installation and Maintenance of Tungsten Alloy Screws
7.1 Installation Guide for Tungsten Alloy Screws
7.1.1 Special Tools and Torque Control Parameters for Tungsten Alloy Screws
7.1.2 Installation Adaptation Schemes for Tungsten Alloy Screws in Extreme Environments
7.2 Maintenance Strategies for Tungsten Alloy Screws
7.2.1 Standardized Process for Regular Inspection of Tungsten Alloy Screws
7.2.2 Diagnosis and Repair Technology for Common Failures of Tungsten Alloy Screws
Appendix
Professional Terminology of Tungsten Alloy Screws
References
Chapter 1 Introduction
Tungsten alloy screws play an indispensable role in modern industry and technology. Their unique high density and durability make them stand out in many application scenarios. This chapter aims to systematically introduce the characteristics and application value of tungsten alloy screws through the definition and overview, concept and function, and comparison with other fasteners. Tungsten alloy is combined with other metals through a specific alloying process to exhibit excellent mechanical properties and is widely used in environments requiring high strength and reliability. From engineering machinery to precision instruments, the emergence of tungsten alloy screws has provided new possibilities for the design and manufacture of equipment. Advances in preparation processes such as powder metallurgy and hot isostatic pressing have further improved their performance consistency, enabling these screws to adapt to complex working conditions. Through continuous material analysis and performance testing, researchers continue to explore its potential application areas, injecting new vitality into industrial development.
1.1 Definition and Overview of Tungsten Alloy Screws
Tungsten alloy screws are specialized fasteners made primarily of tungsten , combined with other metals such as nickel or copper through advanced processing. Their definition stems from their exceptional physical properties and wide range of applications. Tungsten is renowned for its high density and corrosion resistance. When alloyed with other metals, it forms a material that combines strength and toughness, making it particularly suitable for use in demanding environments. An overview of screws requires an understanding of their manufacturing process, which typically involves mixing tungsten powder with other metal powders, pressing and sintering at high temperatures, and finally forming the screws through precision machining. Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is crucial in this process, as it applies uniform pressure to eliminate internal defects and ensure the screw’s structural consistency and reliability. Tungsten alloy screws have applications ranging from heavy machinery to precision electronics, and their high density makes them particularly suitable for compact designs. By adjusting the alloy ratio and processing parameters, manufacturers can tailor the screw’s properties to specific needs, making them flexible and adaptable in industrial production.
The emergence of this type of screw has not only promoted the advancement of fastener technology but also provided a more efficient solution for equipment maintenance and installation. Through in-depth research into the microstructure and mechanical properties of tungsten alloy screws, researchers have discovered impressive stability in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. This stability stems from the inherent properties of tungsten and its synergistic effect with added elements, enabling the screws to withstand the wear and fatigue of long-term use. With the growing demand for high-performance fasteners in industry, tungsten alloy screws have become a highly sought-after research area.
1.1.1 Concept and Function of Tungsten Alloy Screws
Tungsten alloy screw can be understood as a clever combination of tungsten’s high-performance properties and the screw’s fastening function, designed to meet modern industry’s demand for high-strength and durable fasteners. The core concept is to leverage tungsten’s high density and deformation resistance, combining it with metals such as nickel and copper through an alloying process to create a fastener capable of stable operation in complex environments. The concept’s versatility is a key feature. Tungsten alloy screws not only provide mechanical connection but also, under specific conditions, provide vibration damping, balancing, and protection. For example, in precision instruments, the screw’s fastening function ensures precise positioning of components, while its high density helps absorb vibration, reducing noise and instability during equipment operation. Preparation processes such as powder metallurgy ensure uniform distribution of material components through precise control of powder particle size, while hot isostatic pressing further enhances the screw’s internal structure, enabling it to withstand high loads and extreme temperatures.
Tungsten alloy screws is also reflected in their adaptability. Different industrial scenarios have different requirements for screws. Manufacturers can customize screws that meet specific functions by adjusting the alloy ratio and processing technology. For example, in scenarios where high wear resistance is required, the surface of the screw can be specially treated to extend its service life; in situations where high precision is required, the thread design of the screw can be more refined. Through mechanical testing and environmental simulation, researchers have found that tungsten alloy screws perform well in long-term use, and their fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance provide guarantees for the safe operation of equipment. This multifunctional characteristic makes it very popular in engineering design, especially in complex systems that need to balance performance and reliability. The combination of the concept and function of tungsten alloy screws not only enhances the practical value of fasteners, but also opens up new possibilities for future technological innovation.
READ MORE:What Are Tungsten Alloy Screws
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595