Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Overview of Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.2 Composition System of Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.2.1 Tungsten Alloy Sphere Core Matrix: Properties and Requirements of Tungsten
1.2.2 Tungsten Alloy Ball Binder: Roles of Nickel, Iron, and Copper
1.2.3 Functions of Trace Additives in Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.3 Performance Parameters of Tungsten Alloy Balls with Different Compositions
1.4 Common Specifications and Dimensions of Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.5 Basic Applications of Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.6 Development Context of Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.6.1 Early Research and Development Stage (Mid-20th Century – 1980s)
1.6.2 Industrialization Development Stage (1990s – Early 21st Century)
1.6.3 High-performance Upgrade Stage (Since the 21st Century)
Chapter 2 Basic Properties of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.1 Density Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
2.1.1 Density Parameter Range of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
2.1.2 Density Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Balls with Lead, Steel, and Other Materials
2.2 Strength Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.3 Hardness Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.4 Wear Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.5 Thermal Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.6 Electrical Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
2.7 Thermal Stability of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
2.8 Non-magnetic Advantages and Applications of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.9 Neutron Radiation Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
2.10 Gamma-ray Radiation Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
2.11 Factors Affecting the Performance of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.11.1 Effect of Component Ratio on the Performance of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.11.2 Influence of Preparation Process on the Properties of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.11.3 Influence of Subsequent Processing on the Properties of Tungsten Alloy Balls
2.12 MSDS of Tungsten Alloy Balls by CTIA GROUP LTD
Chapter 3 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Balls
3.1 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Balls by Composition
3.1.1 W-Ni-Fe Alloy Spheres
3.1.2 W-Ni-Cu Alloy Spheres
3.1.3 W-Cu Alloy Spheres
3.1.4 W-Ag Alloy Balls
3.1.5 Tungsten Alloy Balls with Other Compositions
3.2 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Balls by Precision
3.2.1 Precision-grade Tungsten Alloy Balls
3.2.2 Ordinary-grade Tungsten Alloy Balls
3.3 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Balls by Application
3.3.1 Counterweight-grade Tungsten Alloy Balls
3.3.2 Shielding-grade Tungsten Alloy Spheres
3.3.3 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Bearings
3.3.4 Tungsten Alloy Health Balls
3.3.5 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Medical Collimators
3.3.6 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Aerospace Inertial Components
3.3.7 Civilian Tungsten Alloy Balls (Such as Fishing Sinkers)
Chapter 4 Preparation Process of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.1 Raw Material Pretreatment of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.1.1 Purification of Tungsten Powder for Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.1.2 Elemental Proportioning and Mixing of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.2 Forming Process of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.2.1 Cold Pressing and Isostatic Pressing of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.2.2 Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of Tungsten Alloy Ball Forming Processes
4.3 Sintering Process of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.3.1 Temperature and Holding Time Control of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.3.2 Advantages of Vacuum Sintering of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.4 Subsequent Processing of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.4.1 Grinding and Polishing of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.4.2 Surface Corrosion-resistant Treatment of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.5 Key Quality Control Points for Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.5.1 Control of Raw Material Purity for Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.5.2 Control of Forming Density Uniformity of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.5.3 Post-sintering Performance Stability Testing of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.6 Quality Inspection of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.6.1 Density Testing of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.6.2 Dimensional Accuracy Inspection of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.6.3 Strength Testing of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.6.4 Hardness Testing of Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.6.5 Shielding Performance Testing of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
4.7 Standard System for Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.7.1 Chinese National Standard (GB/T) for Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.7.2 International Industrial Standards for Tungsten Alloy Balls
4.7.3 Tungsten Alloy Related Standards in Europe, America, Japan, and South Korea
4.7.4 Industry-specific Standards for Tungsten Alloy Balls
Chapter 5 Application Areas of Tungsten Alloy Balls
5.1 Application of Tungsten Alloy Balls in General Counterweights
5.1.1 Tungsten Alloy Ball Counterweights for Engineering Machinery
5.1.2 Tungsten Alloy Ball Counterweights for Sports Equipment
5.1.3 Civilian Tungsten Alloy Balls (Fishing Sinkers, Model Counterweights)
5.1.4 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Oil Drilling Valves and Pipeline Counterweights
5.2 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Balls in Industrial and Precision Machinery Fields
5.2.1 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Precision Mechanical Inertial Components
5.2.2 Tungsten Alloy Balls for High-precision Bearings
5.2.3 Wear-resistant Balls for Vibrating Screens and Separation Equipment
5.2.4 Tungsten Alloy Shot Peening for Spraying and Surface Treatment
5.2.5 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Calibration of Measuring Instruments and Balances
5.3 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Balls in High-end Military and Special Fields
5.3.1 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Collimators in Medical Radiotherapy
5.3.2 Tungsten Alloy Spheres for Radiation Shielding and Neutron Absorption in the Nuclear Industry
5.3.3 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Aerospace Inertial Navigation and Flywheel Applications
5.3.4 Tungsten Alloy Spheres for Kinetic Energy Penetrators and Shaped Charge Projectile Cores
5.3.5 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Satellite Attitude Control Flywheels and Gyroscopes
5.4 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Balls in Emerging and Cutting-edge Fields
5.4.1 Balancing Tungsten Alloy Spheres for Laser Weapons and Directed Energy Systems
5.4.2 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Balancing and Counterweighting of Hypersonic Vehicles
5.4.3 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Deep-sea Exploration Vehicles and Submarines
5.4.4 Tungsten Alloy Balls for Ultrasonic Welding of New Energy Battery Tabs
5.4.5 Tungsten Alloy Balls for 5G Communication Base Station Filter Oscillators
5.4.6 Tungsten Alloy Balls for High-end Watch Rotors and Automatic Winding Mechanisms
Chapter 6 Common Quality Problems and Solutions for Tungsten Alloy Balls
6.1 Causes and Elimination Methods of Surface Cracks in Tungsten Alloy Spheres
6.2 Adjustment and Prevention of Out-of-tolerance Dimensional Deviations of Tungsten Alloy Balls
6.3 Handling of Density Inhomogeneity and Segregation Problems in Tungsten Alloy Spheres
6.4 Improvement of Porosity and Looseness Defects on the Surface of Tungsten Alloy Spheres
6.5 Tungsten Alloy Sphericity and Roundness Correction Technology
6.6 Methods for Adjusting Excessively Low or High Hardness of Tungsten Alloy Balls
6.7 Investigation and Improvement of Internal Inclusion Defects in Tungsten Alloy Spheres
6.8 Treatment of Chipping and Spalling During the Grinding and Polishing Stage of Tungsten Alloy Balls
Appendix
Tungsten Alloy Ball Terminology
References
Chapter 1 Overview of Tungsten Alloy Balls
1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Balls
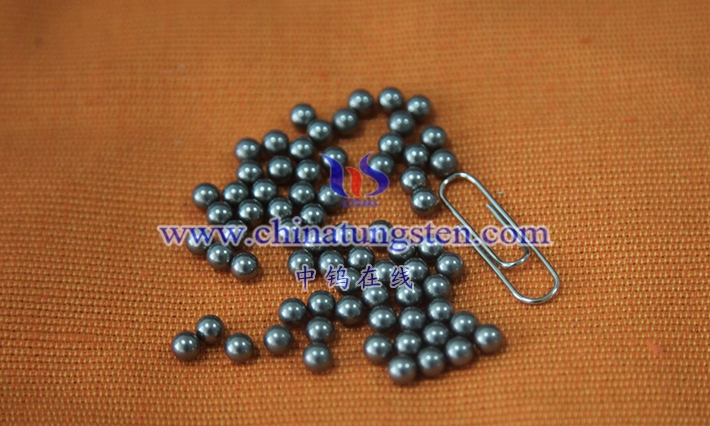
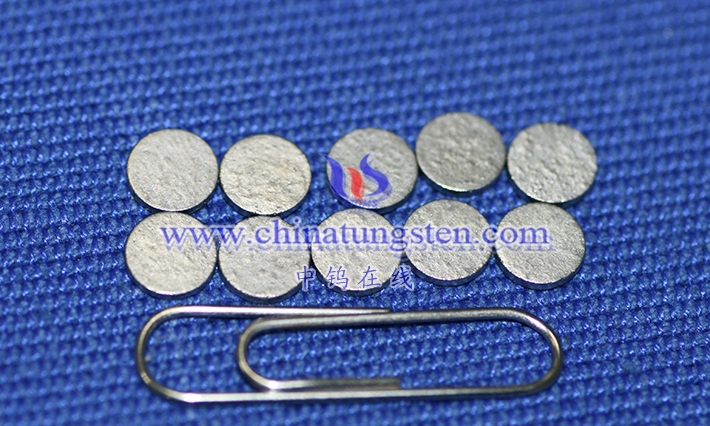
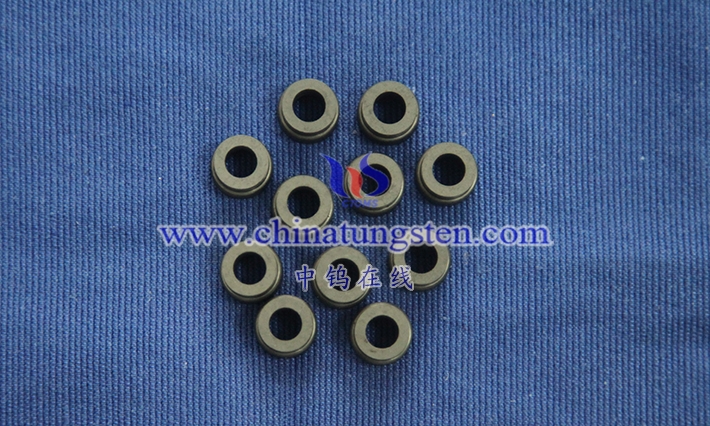
Tungsten alloy spheres are high-density spherical functional components made primarily of tungsten, combined with binder phases such as nickel, iron, and copper using powder metallurgy. They represent a significant extension of typical high- density tungsten-based composite materials in terms of geometry. Unlike traditional steel, ceramic, or lead spheres, tungsten alloy spheres integrate the extremely high density, hardness, and strength of tungsten with the significantly improved toughness, machinability, and environmental adaptability resulting from alloying. This gives them an irreplaceable comprehensive advantage in scenarios requiring large mass, strong shielding, or reliable operation under extreme conditions within a small volume.
From a materials science perspective, tungsten alloy spheres are essentially quasi-isotropic spheres formed by tungsten particles being encapsulated and firmly bonded by a continuous or semi-continuous binder phase. Their microstructure exhibits a typical two-phase characteristic of “hard tungsten particles + tough binder phase”. This structure retains the inherent physicochemical properties of tungsten as a refractory metal, while overcoming the fatal defects of pure tungsten, such as high brittleness and near inability to be plastically formed, through the bridging effect of the binder phase. This allows for the stable production of a complete series of spheres ranging from micrometers to tens of millimeters in size and with precision ranging from ordinary to ultra-precision levels under industrial conditions.
From an engineering application perspective, tungsten alloy balls have long transcended their traditional roles as “counterweight balls” or “bearing balls,” evolving into key structural-functional integrated components that combine high-density counterweight, radiation shielding, inertial energy storage, wear and corrosion resistance, and precision measurement. For this reason, tungsten alloy balls are widely regarded as an indispensable core material in modern aerospace, nuclear medicine imaging, dual-use special munitions, precision instruments, and emerging energy equipment, and their importance continues to increase as equipment develops towards lighter weight, extreme performance, and precision.
1.2 Composition System of Tungsten Alloy Balls
Tungsten alloy spheres can be divided into three layers: a core matrix, a binder phase, and trace functional additives. The proportions and types of these three components directly determine the final sphere’s density, mechanical properties, magnetic characteristics, shielding ability, and environmental adaptability. A well-designed composition allows for precise performance control and optimal functional matching while ensuring high tungsten content, enabling highly specialized product series of tungsten alloy spheres for various applications.
READ MORE:What Are Tungsten Alloy Balls
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595