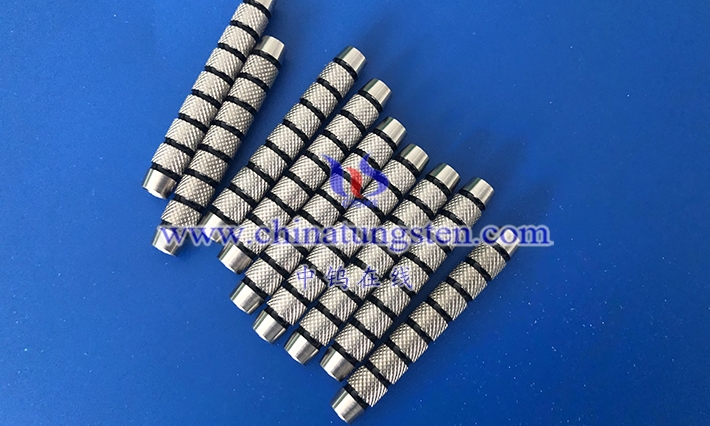
The thermal expansion coefficient of tungsten-nickel-iron alloy is one of its key thermal performance parameters, usually in the range of 4 – 6×10⁻⁶/℃, and the specific value is affected by the alloy composition ratio and microstructure. The thermal expansion coefficient is a physical quantity describing the change of volume or length of a material with temperature when heated. A lower thermal expansion coefficient means that the material has a smaller dimensional change when the temperature fluctuates, which is crucial for application scenarios requiring high precision and dimensional stability.
From the perspective of composition, tungsten has a low thermal expansion coefficient (about 4.5×10⁻⁶/℃), while nickel (about 13.3×10⁻⁶/℃) and iron (about 11.8×10⁻⁶/℃) have relatively high thermal expansion coefficients. Therefore, the higher the tungsten content in the alloy, the closer the overall thermal expansion coefficient is to that of tungsten, showing lower expansion characteristics; on the contrary, if the nickel-iron content increases, the thermal expansion coefficient will rise slightly, but it is still in a low range. This adjustability makes it possible to optimize the thermal expansion coefficient by adjusting the composition according to specific application requirements, so as to match the expansion characteristics of other materials and reduce thermal stress caused by temperature changes.
In terms of microstructure, the tungsten-nickel-iron alloy prepared by powder metallurgy technology has a dense internal structure, and the tungsten particles are closely combined with the nickel-iron binding phase. This structure helps to inhibit the expansion of the material when heated. When the temperature rises, the tungsten particles themselves expand slightly, while the nickel-iron binding phase, although expanding slightly more, is constrained by the surrounding tungsten particles, and the overall expansion is effectively limited, so that the alloy as a whole shows a low thermal expansion coefficient.
In practical applications, this characteristic makes it play an important role in the fields of precision instrument manufacturing and high-temperature components of aerospace equipment. For example, in the gyro rotor of inertial navigation systems, materials need to have an extremely low thermal expansion coefficient to ensure that the rotor size is stable when the temperature changes, thereby maintaining navigation accuracy; in components used with low-expansion materials such as ceramics and glass, the low expansion characteristic of tungsten-nickel-iron alloy can reduce thermal stress at the interface, avoid cracking or loosening, and improve the reliability of the overall structure.
The WeChat public account “China Tungsten Online” updates the prices of various tungstates such as tungstates such as tungstate powder, ammonium tungstate, tungsten products, high-density tungsten alloys, cemented carbides, tungsten concentrates, etc. on a daily basis. At the same time, it provides the most professional WeChat group in the industry for everyone to exchange supply and demand information, and you can exchange information about tungsten powder at any time. Follow “China Tungsten Online” and join the China Tungsten Online WeChat exchange group. Daily tungsten product prices and supply and demand information will be delivered in a timely manner, and real-time communication will be carried out. For more tungsten product market trends, products and information, please follow the “China Tungsten Online” WeChat public account, or visit news.chinatungsten.com to obtain daily updated information.
Contact information: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595
Scan the QR code to follow the “China Tungsten Online” WeChat public account and get real-time updated tungsten, molybdenum and rare earth product market prices and information for free every morning.






