Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Understanding Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
1.1 What Is a Tungsten Alloy Nozzle?
1.1.1 Definition and Basic Components of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
1.1.2 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
1.2 The Value of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles: Why Choose Tungsten Alloy?
1.2.1 Performance Leap of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles Compared to Traditional Nozzles
1.2.2 Value of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in Typical Scenarios
1.3 Basic Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
1.4 Industry Positioning and Application Scenarios of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
1.4.1 The Role of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in the High-End Manufacturing Industry Chain
1.4.2 Typical Application Scenarios of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
Chapter 2 Structure of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1 Key Structural Elements of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.1 Basic Structure of Tungsten Alloy Nozzle: Inlet, Flow Channel and Outlet
2.1.2 Structural Parameters of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.2.1 Orifice Parameters of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.2.2 Cone Angle Parameters of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.2.3 Length Parameters of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.2.4 Multi-Parameter Collaborative Design of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.3 Structural Types of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.3.1 Straight-Hole Tungsten Alloy Nozzle
2.1.3.2 Conical Tungsten Alloy Nozzle
2.1.3.3 Fan-Shaped Tungsten Alloy Nozzle
2.1.3.4 Other Special Structure Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.4 Structural Derivative Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.1.4.1 Flow Stability Brought About by the Flow Channel Structure
2.1.4.2 Influence of Structural Accuracy on Atomization Effect
2.2 Material Specifications of Tungsten Alloy for Nozzles
2.2.1 Common Composition Ratios and Applications of Tungsten Alloys for Nozzles
2.2.1.1 Basic Formula with High Tungsten Content (Tungsten Content ≥ 90%)
2.2.1.2 Tungsten-Nickel-Iron Alloy Proportions
2.2.1.3 Tungsten-Nickel-Copper Alloy Ratio
2.2.1.4 Special Formulation: Customized for Extreme Working Conditions Such as High Temperature and High Pressure
2.2.2 Specifications and Control Requirements for Tungsten Alloys Used in Nozzles
2.2.2.1 Chemical Composition Specifications of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.2.2.2 Physical Property Specifications of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.2.2.3 Mechanical Property Specifications of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
2.2.2.4 Machining Accuracy Specifications for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
Chapter 3 Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.1 Melting Point Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.1.1 Numerical Range and Determination Standards for High Melting Points
3.1.2 The Value of High Melting Point for Adaptability to High-Temperature Operating Conditions
3.2 Density Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.2.1 Typical Density Range and Influencing Factors
3.2.2 The Correlation Mechanism Between High Density and Wear Resistance and Stability
3.3 Hardness Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.3.1 Commonly Used Testing Methods for Hardness Index
3.3.2 Correlation Analysis Between Hardness and Service Life
3.4 Strength Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.4.1 Core Indicators of Tensile Strength and Compressive Strength
3.4.2 Strength Characteristics Under High-Pressure Conditions
3.5 Chemical Stability of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.5.1 Performance in Resisting Acid and Alkali Corrosion
3.5.2 Antioxidant Capacity Under High Temperature Environment
3.6 Thermal Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.6.1 Key Parameter Range of Thermal Conductivity
3.6.2 Influence of Thermal Conductivity on Temperature Distribution and Thermal Deformation
3.7 Electrical Conductivity of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.7.1 Numerical Characteristics of Electrical Conductivity
3.7.2 Adaptability of Conductivity to Specific Application Scenarios
3.8 Wear Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.8.1 Wear Mechanism and Wear Resistance Evaluation Criteria
3.8.2 Material and Structural Optimization Methods to Improve Wear Resistance
3.9 Impact Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.9.1 Test Methods and Indicators for Impact Strength
3.9.2 The Significance of Impact Resistance for Adaptability to Complex Working Conditions
3.10 Dimensional Stability of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.10.1 Dimensional Deformation Laws Under Temperature Changes
3.10.2 Influence of Dimensional Stability on Injection Accuracy
3.11 Radiation Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.11.1 Core Evaluation Indicators of Radiation Resistance Performance
3.11.2 Application Adaptability in Radiation Environments Such as the Nuclear Industry
3.12 Surface Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.12.1 Characteristics of Surface Roughness and Friction Coefficient
3.12.2 The Role of Surface Treatment in Improving Properties
3.13 Fatigue Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
3.13.1 Test Methods and Influencing Factors for Fatigue Life
3.13.2 Fatigue Resistance Performance Under Alternating Load Conditions
3.14 MSDS of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles from CTIA GROUP LTD
Chapter 4 Manufacturing of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
4.1 Raw Material Preparation Process for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles: From Tungsten Ore to Alloy Powder
4.1.1 Tungsten Ore Pretreatment: Beneficiation and Purification Processes
4.1.2 Tungsten Powder Preparation: Reduction Process and Particle Size Control
4.1.3 Alloying Treatment: Key Points of Doping and Mixing Processes
4.1.4 Powder Performance Control: Optimization of Flowability and Bulk Density
4.2 Forming Process of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles: Blank Forming Technology and Selection
4.2.1 Traditional Compression Molding: Compression Process and Parameter Control
4.2.2 Precision Forming Technology: Advantages of Isostatic Pressing Process
4.2.3 Additive Manufacturing Technology: Exploration of 3D Printing Applications
4.2.4 Molding Process Selection: Based on Nozzle Specifications and Batch Requirements
4.3 Sintering Process of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles: Core Technology for Densification
4.3.1 Pre-Firing Treatment: Degreasing and Stress Relief Process
4.3.2 High-Temperature Sintering: Key Parameters for Temperature and Atmosphere Control
4.3.3 Sintering Densification Mechanism: Porosity Control and Performance Correlation
4.3.4 Prevention of Sintering Defects: Measures to Control Cracking and Deformation
4.4 Post-Processing Technology for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles: Improving Precision and Performance
4.4.1 Precision Machining: Flow Channel and End Face Machining Technology
4.4.2 Surface Treatment Processes: Polishing and Coating Enhancement Technologies
4.4.3 Dimensional Calibration: Precision Measurement and Correction Process
4.4.4 Finished Product Cleaning and Drying: Impurity Removal Process Specifications
4.5 Quality Control of Raw Material Stage for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
4.5.1 Tungsten Powder Purity Testing
4.5.2 Test Procedure for Uniformity of Alloy Powder Composition
4.5.3 Testing of Powder Physical Properties
4.6 Quality Control of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles During Forming and Sintering Stages
4.6.1 Methods for Testing the Density and Compactness of the Billet
4.6.2 Composition and Microstructure Analysis of Sintered Body
4.6.3 Sampling and Testing Specifications for Mechanical Properties of Sintered Bodies
4.7 Quality Control of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in Finished Product Stage
4.7.1 Dimensional Accuracy Inspection
4.7.2 Surface Quality Control
4.7.3 Operating Condition Performance Testing
4.8 Quality Control System and Standards for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
4.8.1 Establishment of a Full-Process Quality Traceability System for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
4.8.2 Setting of Key Quality Control Points
4.8.3 Industry Quality Standards and Compliance Requirements
Chapter 5 Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles with Nozzles Made of Other Materials
5.1 Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles and Stainless Steel Nozzles
5.1.1 Comparison of High Temperature Resistance: Temperature Tolerance Range and Stability
5.1.2 Comparison of Wear Resistance: Differences in Wear Rate and Service Life
5.1.3 Comparison of Mechanical Properties: Analysis of the Compatibility Between Strength and Toughness
5.1.4 Economic Comparison: Comprehensive Assessment of Cost and Maintenance Costs
5.2 Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles and Ceramic Nozzles
5.2.1 Comparison of Mechanical Properties: Differences in Impact Strength and Brittleness
5.2.2 Comparison of Wear Resistance: Hard Particle Wear and Abrasive Wear Performance
5.2.3 Comparison of Processing Performance: Molding Accuracy and Adaptability to Complex Structures
5.2.4 Reliability Comparison: Thermal Shock Resistance and Usage Stability Analysis
5.3 Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles and Copper Alloy Nozzles
5.3.1 High-Temperature Strength Comparison: Mechanical Property Retention Rate Under High-Temperature Environments
5.3.2 Service Life Comparison: Differences in Attenuation Patterns Under Different Operating Conditions
5.3.3 Comparison of Thermal Conductivity: Characteristics of Heat Conduction and Temperature Distribution
5.3.4 Corrosion Resistance Comparison: Corrosion Resistance Performance in Acid and Alkali Media
Chapter 6 Application Areas of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
6.1 Application of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in Industrial Manufacturing
6.1.1 Welding and Cutting: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle for High-Temperature Spraying
6.1.2 Surface Coating: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle for Atomization Molding
6.1.3 Metallurgical Casting: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for High-Temperature Melt Flow
6.1.4 Precision Cleaning: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle for High-Pressure Jetting
6.2 Application of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in the Energy and Mining Field
6.2.1 Oil Drilling: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for High-Pressure Rock Breaking
6.2.2 Coal Gasification: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for High-Temperature Reaction
6.2.3 Thermal Power Generation: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Desulfurization and Denitrification
6.2.4 Nuclear Energy Utilization: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Radiation-Resistant Environments
6.3 Application of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in High-End Equipment
6.3.1 Aerospace: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Engine Gas Injection
6.3.2 Rail Transit: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Braking System Cooling
6.3.3 Medical Devices: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Precision Spraying
6.3.4 Electronics Manufacturing: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Chip Packaging
6.4 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in Military and Special Fields
6.4.1 Military Equipment: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Special Spray Systems
6.4.2 Space Launch: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Propulsion Systems
6.4.3 Chemical Emergency Response: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Handling Corrosive Media
6.4.4 Deep-Sea Exploration: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for High-Pressure Environments
6.5 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles in Emerging Fields
6.5.1 3D Printing: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle for Metal Powder Jetting
6.5.2 Hydrogen Energy Industry: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Fuel Cells
6.5.3 Carbon Capture: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle for Absorbent Injection
6.5.4 Laser Technology: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles for Auxiliary Cooling
Chapter 7 Selection, Installation and Maintenance of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.1 Scientific Selection of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.1.1 Matching of Operating Parameters: Adaptation of Tungsten Alloy Nozzle to Temperature and Pressure
7.1.2 Media Characteristics Compatibility: Tungsten Alloy Nozzles Are Compatible with Corrosive Media
7.1.3 Performance Requirements Matching: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle and Flow Atomization Adaptation
7.1.4 Structural Type Selection: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Structure and Scene Adaptation
7.1.5 Avoiding Common Selection Mistakes: Analysis of Common Issues in Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Selection
7.2 Installation and Adjustment of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles: Key Points for Precision Assurance
7.2.1 Pre-Installation Preparation: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Inspection and Accessory Compatibility
7.2.2 Core Installation Specifications: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Positioning and Sealing Technology
7.2.3 Installation Accuracy Control: Coaxiality and Perpendicularity Calibration of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.2.4 Core Debugging Process: Calibration of Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Flow and Pressure
7.2.5 Installation, Commissioning and Acceptance: Performance Verification Standards for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.3 Daily Maintenance of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.3.1 Key Points for Regular Inspection: Wear and Corrosion Detection of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.3.2 Cleaning and Maintenance Standards: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Clog Cleaning and Surface Maintenance
7.3.3 Maintenance Cycle Determination: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Maintenance Plan Based on Operating Conditions
7.3.4 Management of Consumable Parts: Replacement and Stockpiling Strategy for Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Parts
7.4 Troubleshooting for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.4.1 Common Fault Diagnosis: Analysis of the Causes of Abnormal Flow Rate in Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.4.2 Troubleshooting: Repair Solution for Wear and Leakage of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.4.3 Extreme Failure Handling: Measures for Treating Cracks and Deformation of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
7.4.4 Fault Prevention System: Risk Management Throughout the Life Cycle of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
Chapter 8 Common Problems with Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
8.1 Common Problems in the Manufacturing of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
8.1.1 Raw Material Preparation Issues: Insufficient Purity and Excessive Impurities in Tungsten Powder
8.1.2 Molding Process Issues: Cracking and Uneven Density of the Billet
8.1.3 Problems in the Sintering Process: Deformation and Insufficient Density of the Sintered Body
8.1.4 Post-Processing Issues: Substandard Flow Channel Precision and Surface Defects
8.2 Common Problems in Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Selection and Adaptation
8.2.1 Operating Condition Matching Problem: Temperature and Pressure Mismatch with Nozzle Performance
8.2.2 Structural Selection Issue: The Flow Channel Type Does Not Match the Atomization Requirements
8.2.3 Material Compatibility Issues: Incompatibility Between Alloy Composition and Corrosive Media
8.2.4 Specification Selection Issues: Mismatch Between Orifice Diameter Parameters and Flow Rate Requirements
8.3 Common Problems in the Installation and Use of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
8.3.1 Installation and Operation Issues: Positioning Deviation and Inadequate Sealing
8.3.2 Problems Caused by Improper Debugging: Inaccurate Flow and Pressure Calibration
8.3.3 Operating Condition Adaptation Issue: Performance Degrades Too Quickly Under Extreme Environments
8.3.4 Collaborative Operation Issues: Insufficient Compatibility with Supporting Equipment
8.4 Common Problems in the Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
8.4.1 Problems Caused by Improper Maintenance: Incomplete Cleaning and Oversights in Inspection
8.4.2 Wear and Corrosion Problems: Abnormal Wear and Severe Localized Corrosion
8.4.3 Fault Diagnosis Issues: Misjudgment of Abnormal Flow and Leakage Causes
8.4.4 Replacement and Upgrade Issues: Untimely Replacement of Vulnerable Parts and Mismatched Models
Appendix
Appendix A: Chinese Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Standard
Appendix B: International Standards for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
Appendix C: Tungsten Alloy Nozzle Standards of Europe, America, Japan, South Korea, and Other Countries
Appendix D: Terminology Table for Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
References
Chapter 1 Understanding Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
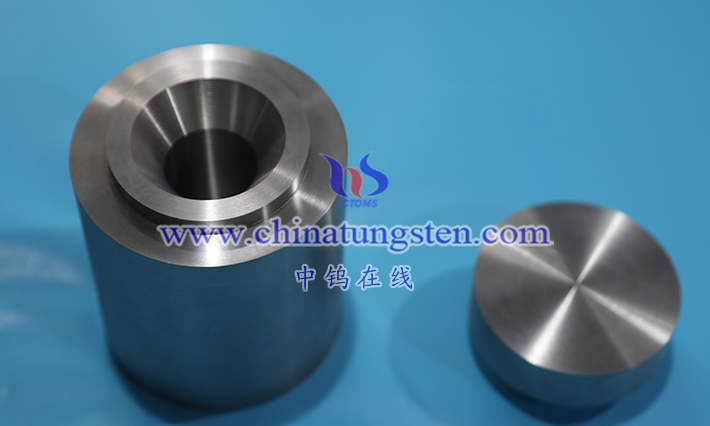
1.1 What is a tungsten alloy nozzle
Tungsten alloy nozzles are high-density, high-strength, and wear-resistant functional components with a specific flow channel structure. They are made primarily of tungsten (typically with a mass fraction of over 85%), with the addition of binder phases such as nickel, iron, copper, cobalt, or molybdenum , and manufactured using powder metallurgy liquid-phase sintering processes. Under extreme operating conditions, they are crucial for the directional jetting of high-pressure gases, liquids, molten particles, or plasma at extremely high speeds, with extremely high precision and extremely low divergence angles. Simultaneously, they must withstand long-term attacks from high-temperature oxidation, abrasive erosion, cavitation fatigue, thermal shock cracking , and the combined onslaught of highly corrosive media. Compared to traditional cemented carbide, zirconia ceramic, stainless steel, titanium alloy, and even pure tungsten nozzles, tungsten alloy nozzles have achieved a qualitative leap in hardness, toughness, density, temperature resistance limit, erosion resistance life, and overall cost-effectiveness. They have become the most core and demanding throat actuators in cutting-edge processes such as thermal spraying, high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) spraying, plasma spraying, cold spraying, high-pressure water jet cutting, laser cladding powder feeding, diesel common rail fuel injection, gas turbine combustion chambers, industrial sandblasting and rust removal, precision atomization , and plasma generators.
The emergence of tungsten alloy nozzles is essentially a product of the deep integration of materials science with multiple disciplines such as fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and surface engineering. It not only inherits tungsten’s extremely high melting point, hardness, and resistance to softening, but also overcomes the inherent brittleness of pure tungsten and ceramics through the introduction of a ductile binder phase , achieving an ideal combination of “hardness and toughness.” Simultaneously, the high density results in enormous mass inertia and heat capacity, allowing it to maintain millisecond-level geometric stability even under high-speed jet recoil and high-temperature thermal shock. Controllable magnetism and excellent thermal conductivity enable it to operate safely in strong electromagnetic fields or high-power thermal load environments. It is this ultimate balance of multidimensional properties that makes tungsten alloy nozzles stand out from numerous candidate materials, becoming the “choke point guardian” for today’s industrial processes with the highest requirements for spray precision, service life, and operational reliability.
From a broader perspective, tungsten alloy nozzles represent a typical extension of high-density alloys in terms of functionality, precision, and extreme applications. They are no longer simply wear-resistant parts, but rather system-level key components integrating energy conversion, mass transfer, surface modification, and environmental shielding. A seemingly insignificant nozzle often determines whether equipment worth hundreds of millions of yuan on an entire production line can operate stably, whether the coating quality meets aerospace-grade standards, whether waterjet cutting precision reaches the micron level, and whether fuel atomization achieves ultra-low emissions. Therefore, the understanding of tungsten alloy nozzles should not be limited to “a nozzle made of a wear-resistant material,” but should be elevated to the strategic level of “the most vulnerable yet most important link in the modern high-end manufacturing process chain.” Only by deeply understanding the coupling mechanism of its materials-structure-process-environment can we truly grasp the initiative in its design, manufacturing, and application.
READ MORE:What Is Tungsten Alloy Nozzles
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595