Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Entering the World of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.1 Concept of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.1.2 Basic Constituent Elements of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.1.3 Basic Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.2 Material Selection Logic of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.2.1 Performance Comparison Between Tungsten Alloys and Mainstream Shielding Materials
1.2.2 Core Advantages of Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.2.3 Selection Logic of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Under Scene Adaptation
1.3 Development History and Industrial Value of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.3.1 Technological Evolution Stages of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.3.2 Technological Breakthrough Nodes of Tungsten Alloys in Shielding Can Applications
1.3.3 Reflection of Core Supporting Value of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Industrial End
Chapter 2 Shielding Mechanism and Performance Indicators of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.1 Basic Principles of Radiation Shielding of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.1.1 Analysis of Propagation Characteristics of Ionizing Radiation Addressed by Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.1.2 Shielding Mechanism (Absorption and Attenuation) of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.1.2.1 Correlation Between Tungsten Atomic Structure and Shielding Performance of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.1.2.2 Action Process of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans on Different Radiations
2.1.2.3 Optimization Effect of Alloy Composition on Shielding Mechanism of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.1.3 Analysis of Factors Affecting Shielding Effect of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.1.3.1 Intrinsic Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Materials
2.1.3.2 Factors of Shielding Structure Design Parameters
2.1.3.3 Characteristics of Radiation Source Itself
2.1.3.4 Influencing Factors of Service Environment Conditions
2.1.3.5 Factors of Manufacturing Process Precision Control
2.2 Key Performance Indicator System of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.1 Density Indicator of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.2 Hardness Indicator of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.3 Tensile Strength Indicator of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.4 Sealing Performance Indicator of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.5 Corrosion Resistance Indicator of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.6 Shielding Efficiency of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.7 Ductility Indicator of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.2.8 High-Temperature Resistance Indicator of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
2.3 MSDS of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans by CTIA GROUP LTD
Chapter 3 Design Logic and Type Classification of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.1 Structural Composition of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.1.1 Main Shielding Structure of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans (Can Body, Can Cover)
3.1.2 Auxiliary Functional Structure of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans (Lining, Connecting Parts)
3.1.3 Shielding Principle of Structural Coordination of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.2 Main Types of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Classified by Shielding Scenarios
3.2.1 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Specialized for Nuclear Industry
3.2.2 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Specialized for Medical Field
3.2.3 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Specialized for Industrial Testing
3.3 Common Types of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Classified by Structural Form
3.3.1 Fixed Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.3.2 Portable Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.3.3 Sealed Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.3.4 Open Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.3.5 Single-Layer Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.3.6 Multi-Layer Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.3.7 Integrated Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
3.3.8 Modular Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
Chapter 4 Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.1 Composition and Requirements of Raw Materials for Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.1.1 Main Raw Material Ratio of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.1.2 Purity and Particle Size Requirements of Raw Materials for Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.1.3 Selection Standards and Requirements of Auxiliary Materials for Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.2 Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.2.1 Basic Powder Metallurgy Process of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans (Powder Preparation, Mixing, Pressing)
4.2.2 Key Sintering Process and Parameter Control of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.2.3 Machining Process of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.2.4 Surface Treatment Process of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.3 Quality Control Points in Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.3.1 Incoming Inspection Standards and Methods for Raw Materials of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.3.2 Quality Inspection Nodes in Intermediate Processes of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
4.3.3 Full-Item Inspection Process for Finished Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Before Delivery
Chapter 5 Application Fields of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
5.1 Application of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Nuclear Industry
5.1.1 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Spent Fuel Storage and Transportation
5.1.2 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Radioactive Waste Treatment
5.1.3 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Nuclear Geological Exploration Samples
5.1.4 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Nuclear Reactor Auxiliary Equipment
5.2 Application of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Medical and Health Field
5.2.1 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Radioactive Drug Storage and Transportation
5.2.2 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Radiation Therapy Sources
5.2.3 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Supporting Medical Imaging Equipment
5.2.4 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Temporary Storage of Radioactive Waste
5.2.5 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for In Vitro Diagnostic Reagent Protection
5.3 Application of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Industrial Testing and Electronic Field
5.3.1 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Industrial Radiographic Inspection Sources
5.3.2 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Electronic Component Anti-Interference
5.3.3 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Semiconductor Manufacturing Testing
5.3.4 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Non-Destructive Testing Equipment
5.3.5 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Precision Electronic Instrument Protection
5.4 Application of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Aerospace Field
5.4.1 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Aerospace Radiation Tests
5.4.2 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Aerospace Component Protection
5.4.3 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Aerospace Material Testing
5.5 Application of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Scientific Research Experiment Field
5.5.1 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Nuclear Physics Experiment Samples
5.5.2 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Particle Physics Experiments
5.5.3 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Environmental Radiation Monitoring
5.6 Application of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Other Special Fields
5.6.1 Custom Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Special Environments
5.6.2 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Specialized for National Defense and Military Industry
5.6.3 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Geological Exploration and Mining
5.6.4 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Aerospace Radiation Tests
5.6.5 Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Nuclear Physics Experiment Samples
5.6.6 Application of Custom Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans for Special Environments
Chapter 6 Selection, Use and Maintenance of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.1 Scientific Selection Method of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.1.1 Selection Basis of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Based on Radiation Characteristics
6.1.2 Selection Points of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Based on Service Scenarios
6.1.3 Selection Verification of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans Based on Industry Standards
6.2 Safe Operation Specifications During Use of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.2.1 Basic Operation Procedures and Specifications of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.2.2 Safety Requirements for Movement and Transportation of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.2.3 Emergency Disposal and Fault Handling of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.3 Daily Maintenance and Service Life Extension Skills of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.3.1 Routine Cleaning and Maintenance Methods of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.3.2 Regular Inspection and Performance Calibration of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
6.3.3 Replacement and Maintenance of Vulnerable Parts of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
Chapter 7 Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Other Shielding Cans
7.1 Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Lead Alloy Shielding Cans
7.1.1 Performance Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Lead Alloy Shielding Cans (Shielding Efficiency, Density, Etc.)
7.1.2 Environmental Friendliness Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Lead Alloy Shielding Cans
7.1.3 Applicable Scenario Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Lead Alloy Shielding Cans
7.1.4 Whole-Life Cycle Cost Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Lead Alloy Shielding Cans
7.2 Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Steel Shielding Cans
7.2.1 Shielding Performance Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Steel Shielding Cans
7.2.2 Mechanical Performance Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Steel Shielding Cans
7.2.3 Environmental Adaptability Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Steel Shielding Cans
7.2.4 Cost-Effectiveness Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Steel Shielding Cans
7.3 Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Composite Shielding Material Cans
7.3.1 Material Composition Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Composite Shielding Material Cans
7.3.2 Shielding Mechanism Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Composite Shielding Material Cans
7.3.3 Stability Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Composite Shielding Material Cans
7.3.4 Application Prospect Comparison Between Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans and Composite Shielding Material Cans
Appendices:
Appendix A Chinese Standards for Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
Appendix B International Standards for Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
Appendix C Standards for Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans in Europe, America, Japan, South Korea and Other Countries
Appendix D Glossary of Terms for Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
References
Chapter 1 Entering the World of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
1.1 Concept of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Can
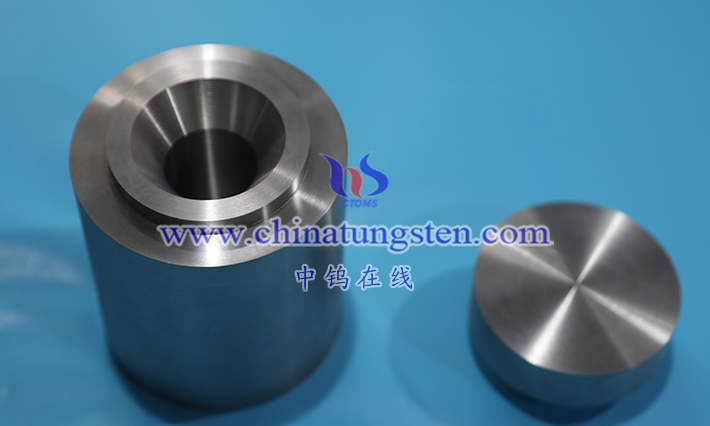
Tungsten alloy shielding containers are functional containers designed and manufactured specifically for containing and shielding radioactive materials, using tungsten-based high-density alloys as the main material in modern radiation protection engineering . They fully utilize the significantly higher bulk density of tungsten alloys compared to lead, iron, or concrete, as well as their superior attenuation capabilities for gamma rays, X-rays, and neutron fluxes, achieving highly efficient radiation shielding within a very limited space. Simultaneously, they possess sufficient structural strength, thermal stability, chemical inertness, and long-term containment reliability. Compared to traditional shielding methods, tungsten alloy shielding containers completely break the inherent contradiction of “better protection, larger volume, and heavier weight,” significantly reducing the overall volume and mass for the same level of protection, thereby improving the space utilization, operational flexibility, and personnel accessibility of the facility.
In practical applications, tungsten alloy shielding containers serve as both the first physical containment barrier for radioactive sources or radioactive waste and a core engineering barrier for radiation dose control. They are widely used around nuclear medicine imaging equipment, isotope production hot chambers, industrial X-ray inspection darkrooms, irradiation channels in research reactors, high-energy physics experimental terminals, and in the temporary storage and transfer of radioactive waste, becoming a key physical component for achieving the principles of “optimal protection” and “minimized dose.” As radiation applications evolve towards higher activity, compactness, and mobility, tungsten alloy shielding containers have gradually replaced traditional lead containers, lead glass containers, and heavy concrete containers, becoming the recognized representative of high-end, green, and long-life shielding solutions in the field of radiation protection today.
1.1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Shielded Can
A tungsten alloy shielding container is strictly defined as a composite engineering container made of tungsten-nickel-iron, tungsten-nickel-copper, or tungsten-nickel-iron-copper high-density alloys with a tungsten content of not less than 90%, manufactured through near-net-shape forming sintering, forging, or precision machining processes, possessing both radioactive material containment and radiation shielding functions. Its design must simultaneously meet the mechanical and thermal requirements of the International Atomic Energy Agency for radioactive material transport containers, the type approval conditions of national nuclear safety regulatory authorities for storage and handling containers, and the most stringent surface dose rate limits for medical and industrial radiation protection.
READ MORE:What Are Tungsten Alloy Shielding Cans
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595






