Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Overview of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.1.1 Structural Features of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.1.2 Basic Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.1.3 Positioning of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Materials Science
1.2 Analysis of Main Elements in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.2.1 Role of Tungsten in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.2.2 Integration of Auxiliary Metal Elements in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.2.2.1 Effect of Nickel Addition on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.2.2.2 Effect of Iron Addition on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.2.2.3 Mechanism of Copper Doping in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.2.2.4 Mechanism of Other Element Doping in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.3 Microstructure of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.3.1 Influence of Crystal Structure on Performance of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.3.2 Observation of Phase Separation Phenomenon in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.4 Theoretical Foundation of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.4.1 Application of Alloy Phase Diagrams in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
1.4.2 Influence of Thermodynamic Principles on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Chapter 2 Classification and Related Analysis of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
2.1 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars Based on Composition
2.1.1 High-Density Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
2.1.2 Low-Density Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
2.1.3 Rare Earth Element Doped Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
2.2 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars Based on Application
2.2.1 Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars for Mechanical Processing Field
2.2.2 Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars for Precision Instrument Field
2.2.3 Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars for High-Temperature Environments
2.2.4 Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars for Wear Environments
2.3 Performance Difference Analysis of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bar Types
2.3.1 Influence of Composition Changes on Physical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
2.3.2 Embodiment of Application-Oriented Design in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
2.3.3 Regulation of Microstructure Differences on Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Chapter 3 Preparation Process of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.1 Powder Metallurgy Method for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.1.1 Raw Material Preparation Steps in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bar Preparation
3.1.1.1 Purification and Particle Size Control of Tungsten Powder
3.1.1.2 Uniformity of Alloy Element Mixing
3.1.2 Influence of Sintering Process on Density of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.1.3 Optimization of Pressing Forming Technology in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.1.4 Role of Liquid Phase Sintering in Densification of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.2 Mechanical Processing Technology for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.2.1 Application of Forming in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.2.2 Application of Plastic Deformation in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.2.3 Optimization of Microstructure by Heat Treatment in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.2.4 Application of Precision Grinding Process in Surface Processing of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.2.5 Application of Electrical Discharge Machining in Achieving Complex Shapes of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.3 Characterization and Quality Control of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.3.1 Use of Microscopy Analysis in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.3.2 Identification of Composition by Spectroscopy Methods in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.3.3 Importance of Density Testing in Quality Assessment of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.3.4 Detection of Internal Defects by Non-Destructive Testing Technology in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.4 Innovative Methods in Preparation Process of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.4.1 Potential of Injection Molding in Production of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
3.4.2 Influence of Additive Manufacturing Technology on Customization of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Chapter 4 Physical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.1 Density and Thermal Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.1.1 Principle of Density Measurement in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.1.2 Contribution of Thermal Expansion Coefficient to Stability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.1.2.1 Thermal Behavior of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars Under High-Temperature Conditions
4.1.2.2 Response of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Low-Temperature Environments
4.1.3 Application of Differential Scanning Calorimetry in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.1.4 Quantification of Thermal Conductivity Measurement for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.1.5 Role of Specific Heat Capacity in Thermal Management of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.2 Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.2.1 Performance of Electrical Conductivity in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.2.2 Implications of Magnetic Parameters for Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.2.3 Influence of Temperature Coefficient of Resistance on Electrical Stability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.2.4 Observation of Hysteresis Loop Analysis in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.3 Optical and Radiation Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.3.1 Relevance of Reflectivity Analysis in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.3.2 Assessment of Radiation Tolerance for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.3.3 Characterization of Absorption Spectrum in Optical Performance of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.3.4 Contribution of Neutron Absorption Cross-Section to Radiation Shielding of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
4.4 MSDS of CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Chapter 5 Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1 Strength and Hardness of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.1 Methods of Tensile Strength Testing in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.1.1 Fracture Mechanism of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars Under Static Loading
5.1.1.2 Influence of Dynamic Loading on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.2 Quantification of Vickers Hardness in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.3 Assessment by Tensile Experiments on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.4 Assessment by Compression Testing on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.4.1 Research on Strain Rate Influence in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.4.2 Insights from Fracture Analysis on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.1.5 Supplementary Verification of Bending Strength on Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.2 Toughness and Fatigue Behavior of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.2.1 Role of Impact Toughness in Durability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.2.2 Application of Cyclic Fatigue Analysis in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.2.3 Methods of Fracture Toughness Measurement in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.2.4 Prediction of High-Cycle Fatigue on Life of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.3 Friction and Wear Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.3.1 Optimization by Friction Coefficient Measurement for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.3.2 Discussion of Wear Mechanisms in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.3.3 Analysis of Abrasive Wear on Surface Damage of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
5.3.4 Performance of Adhesive Wear in Contact Process of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Chapter 6 Corrosion and Durability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.1 Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.1.1 Use of Polarization Curves in Corrosion Research of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.1.2 Protection by Passive Layer Formation on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.1.2.1 Stability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Acidic Environments
6.1.2.2 Response of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars Under Alkaline Conditions
6.1.3 Characterization by Corrosion Potential Measurement for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.1.4 Application of Impedance Spectroscopy in Corrosion Kinetics of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.1.5 Oxidation Reactions on Corrosion Behavior of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.1.6 Regulation of Environmental Factors on Chemical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.2 High-Temperature Oxidation Mechanism of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.2.1 Influence of Oxidation Kinetics on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.2.2 Application of Protective Coatings in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.2.3 Destruction by Volatile Oxide Formation on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.2.4 Regulation of Alloy Elements on Oxidation Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.3 Environmental Durability Testing of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.3.1 Assessment by Salt Spray Testing on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.3.2 Role of Humidity Cycling in Durability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.3.3 Integration of Multi-Scale Simulation in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
6.3.4 Sensitivity Testing of Stress Corrosion Cracking on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Chapter 7 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
7.1 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Riveting Processes
7.1.1 Mechanical Role of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Rivet Forming Process
7.1.2 Interaction Mechanism Between Bucking Bar and Rivet Material
7.1.2.1 Analysis of Contact Stress Distribution in Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
7.1.2.2 Influence of Deformation Coordination on Durability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
7.1.3 Requirements of High-Strength Riveting on Performance of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
7.1.4 Adaptability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Automated Riveting Equipment
7.2 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Aerospace Structural Connections
7.2.1 Selection Principles of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Titanium Alloy Riveting
7.2.2 Demand for Surface Characteristics of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Composite Material Riveting
7.2.3 Stability Analysis of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars Under Vibration Environments
7.2.4 Special Requirements of Low-Temperature Riveting Processes on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
7.3 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Automotive and Rail Transit Manufacturing
7.3.1 Adaptability of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Lightweight Body Riveting
7.3.2 Examination of Wear Behavior of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in High-Frequency Riveting Processes
7.3.3 Compatibility of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Multi-Material Connections
7.4 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Precision Mechanical Assembly
7.4.1 Requirements of Micro-Riveting on Dimensional Accuracy of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
7.4.2 Role of Surface Modification in Precision Applications of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
7.4.3 Demand for Material Purity of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Clean Room Environments
Chapter 8 Common Problems of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.1 Defect Formation in Preparation Process of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.1.1 Influence of Uneven Sintering on Microstructure of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.1.2 Sources and Control of Impurity Contamination in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.1.3 Mechanism of Crack Initiation in Pressing Stage of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.1.4 Cause Analysis of Porosity Residual in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.2 Failure Modes in Use of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.2.1 Fracture Mechanism Caused by Mechanical Overload in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.2.2 Cumulative Effect of Wear and Fatigue in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.2.3 Reduction of Life by Corrosive Environments on Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.2.4 Cracking Phenomenon Caused by Thermal Shock in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.2.5 Influence of Surface Spalling on Function of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.3 Performance Optimization and Fault Diagnosis of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.3.1 Mitigation of Common Problems by Composition Adjustment in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.3.2 Application of Non-Destructive Testing Methods in Defect Identification of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.3.3 Improvement of Durability by Heat Treatment Process in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.3.4 Enhancement of Wear Resistance by Surface Strengthening Technology in Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.3.5 Role of Failure Case Analysis in Optimization of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.4 Performance Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars with Other Bucking Bar Materials
8.4.1 Performance Comparison Between Cemented Carbide Bucking Bars and Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.4.2 Performance Comparison of Steel Bucking Bars Substituting Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
8.4.3 Performance Comparison of Ceramic Material Bucking Bars with Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Appendices:
Appendix A Chinese Standards for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Appendix B International Standards for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars
Appendix C Standards for Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bars in Europe, America, Japan, Korea, etc.
Appendix D Glossary of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Bucking Bar Terms
References
Chapter 1 Overview of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Tops
1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Rivet Top Rod
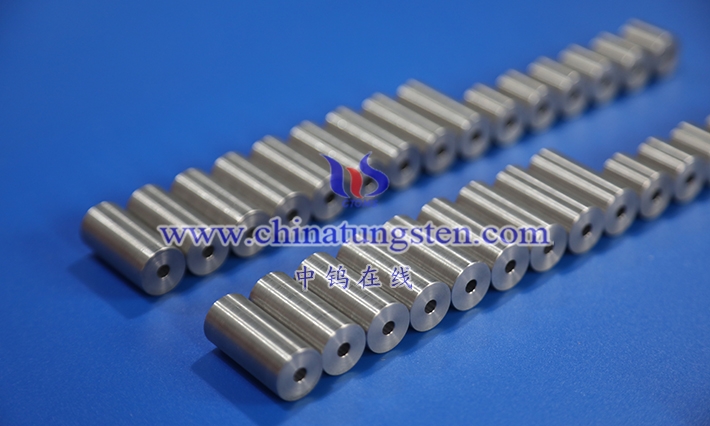
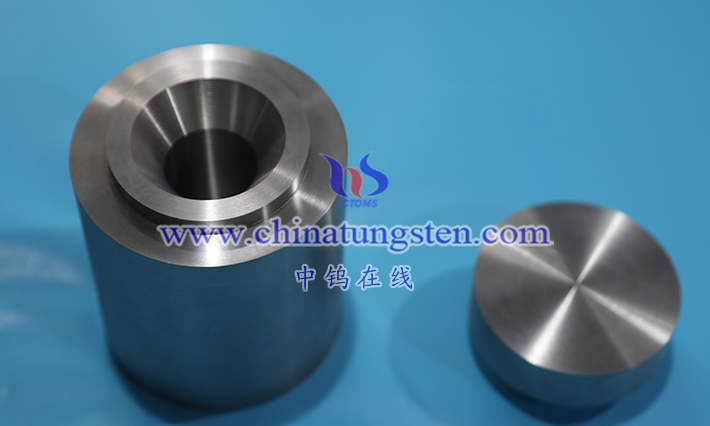
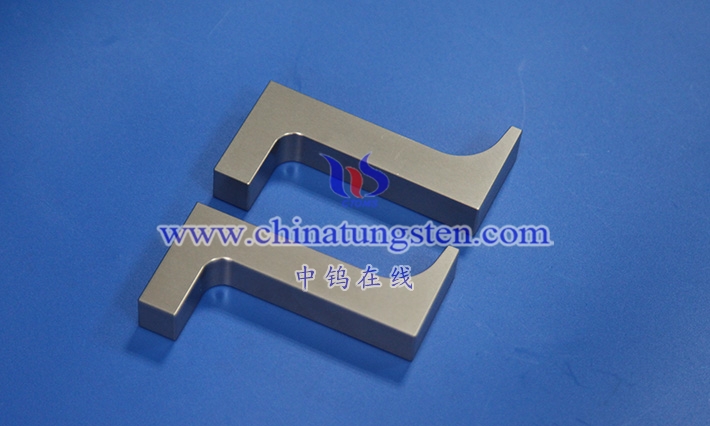
Tungsten alloy rivet mandrels are alloy products with tungsten as the main component. They are typically manufactured using powder metallurgy and machined into specific rod- shaped tools, primarily used for support and shaping during the riveting process. These mandrels are placed at the rivet tail during installation, acting as a reverse support to withstand hammering or pressure, allowing the rivet head to deform smoothly and form a secure connection. Tungsten alloy is chosen for its high density and hardness, enabling it to maintain shape stability under repeated impacts while possessing a certain degree of toughness to prevent brittle fracture. The diameter and length of the mandrel are designed according to the rivet specifications, and its surface is often precision ground to ensure a good fit with the rivet tail.
Tungsten alloy mandrels commonly use tungsten -nickel-iron or tungsten-nickel-copper alloys. The binder phase provides the necessary plasticity, making the mandrel less prone to cracking during processing and use. The preparation process includes powder mixing, pressing, sintering, and thermomechanical processing, with final heat treatment to adjust the microstructure. The working surface of the mandrel needs to be smooth and flat to reduce friction and damage during rivet deformation. The emergence of tungsten alloy mandrels has solved the problem of insufficient durability of traditional steel mandrels in high-strength rivet applications, especially in applications requiring multiple uses, where their lifespan is more stable.
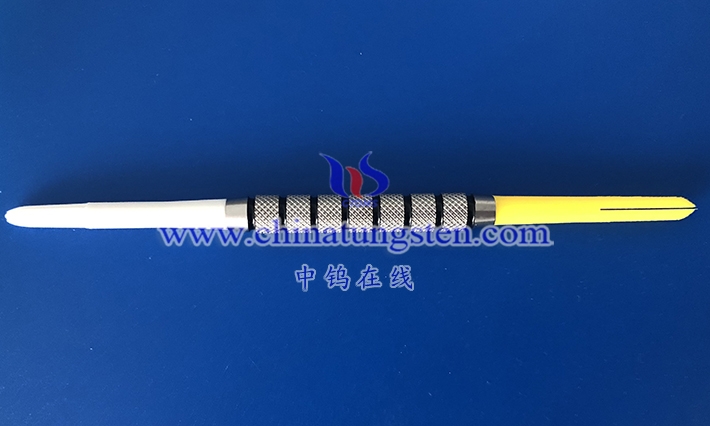
From a functional perspective, tungsten alloy rivet setters not only provide mechanical support but also, through their high density, help concentrate energy transmission, resulting in more uniform rivet deformation. The setter’s end face shape is diverse, such as flat, concave , or convex , to accommodate different rivet types. In use, the setter is fixed to a pneumatic or manual riveting gun, and the operator controls the force to achieve the connection. Maintenance of tungsten alloy setters is relatively simple; regular inspection of surface wear and polishing are sufficient. In conclusion, as an important component of riveting tools, tungsten alloy rivet setters , with their material advantages, improve the efficiency and quality of the connection process and are gradually gaining recognition in the industrial assembly field.
1.1.1 Structural features of tungsten alloy rivet top bars
Tungsten alloy rivet mandrels are mainly reflected in their rod-shaped shape and internal two-phase microstructure. The external design emphasizes functional adaptability, while the internal microstructure determines durability. The mandrel is cylindrical in shape, with one end serving as the working surface for direct contact with the rivet tail, and the other end as a gripping or fixing end for easy installation in riveting equipment. The working surface is typically flat or has shallow grooves to better accommodate rivet tail deformation, and the smooth sides reduce operating resistance. The length and diameter ratio is matched to the rivet size to ensure stable support without interfering with surrounding components.
The internal structure exhibits typical tungsten alloy dual-phase characteristics, with tungsten particles forming a continuous skeleton as the hard phase, and binder phases such as nickel-iron or nickel-copper filling the gaps, providing connectivity and toughness. This microstructure is formed through a sintering process, with nearly spherical tungsten particles and a uniformly distributed binder phase to prevent stress concentration. After hot working, the microstructure displays a fibrous texture, aligned axially to enhance longitudinal strength. The surface is finely ground, resulting in low roughness and reduced rivet adhesion.
READ MORE:What Are Tungsten Alloy Rivet Top Bars
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595