Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Basic Understanding of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
1.1 Concept of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
1.1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
1.1.2 Differentiation from Related Materials
1.2 Development and Research Significance of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
1.2.1 Development Context Based on Tungsten Resource Utilization
1.2.2 Value of Studying Tungsten Alloy Sheets from a Chemical Engineering Perspective
1.2.3 Status of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Application Fields
Chapter 2 Classification System of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
2.1 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Sheets by Material Composition
2.1.1 Nickel-Iron Series Tungsten Alloy Sheets
2.1.2 Nickel-Copper Series Tungsten Alloy Sheets
2.1.3 Tungsten-Copper Alloy Sheets
2.1.4 Tungsten-Silver Alloy Sheets
2.1.5 Other Binder Phase Tungsten Alloy Sheets
2.2 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Sheets by Core Properties
2.2.1 High-Density Tungsten Alloy Sheets
2.2.2 High-Hardness Tungsten Alloy Sheets
2.2.3 Corrosion-Resistant and Wear-Resistant Tungsten Alloy Sheets
2.3 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Sheets by Size Specifications
2.3.1 Ultra-Thin Tungsten Alloy Sheets (Thickness < 0.1mm) 2.3.2 Conventional Thickness Tungsten Alloy Sheets (0.1-10mm) 2.3.3 Thick-Walled Tungsten Alloy Sheets (Thickness > 10mm)
2.3.4 Special-Shaped Size Tungsten Alloy Sheets (Customized)
2.4 Classification of Tungsten Alloy Sheets by Application Scenarios
2.4.1 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for National Defense and Military Industry
2.4.2 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Industrial Manufacturing
2.4.3 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Nuclear and Medical Applications
2.4.4 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Electronic Information
2.4.5 Other Specialized Tungsten Alloy Sheets
Chapter 3 Alloying Principles and Composition Systems of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.1 Chemical Principles of Alloying in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.1.1 Phase Diagram Analysis of Tungsten with Other Metal Elements
3.1.2 Solid Solution Strengthening and Dispersion Strengthening Chemical Mechanisms
3.1.3 Formation Conditions and Stability of Alloy Phases
3.2 Roles and Proportions of Constituent Elements in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.2.1 Synergistic Mechanism of Nickel-Iron System in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.2.2 Synergistic Mechanism of Nickel-Copper System in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.2.3 Doping Effects of Trace Elements in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.3 Chemical Rules for Composition Design of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.3.1 Performance-Oriented Composition Optimization Logic for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.3.2 Chemical Control Methods for Composition Uniformity in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.3.3 Effects of Impurity Elements on Properties of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
3.3.4 Methods for Removing Impurity Elements in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
Chapter 4 Structure-Property Relationships of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.1 Microstructure of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.1.1 Grain Structure and Grain Boundary Chemical Composition
4.1.2 Distribution and Chemical State of Alloy Phases
4.1.3 Chemical Causes of Defect Structures
4.2 Properties and Mechanisms of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.2.1 Chemical Atomic Packing Principle of High Density in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.2.2 Chemical Carrier Mechanism of Thermal and Electrical Conductivity in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.2.3 Chemical Structural Support for Thermal Stability of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.3 Correlation Between Mechanical and Chemical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.3.1 Relationship Between Hardness of Tungsten Alloy Sheets and Chemical Bond Strength
4.3.2 Chemical Corrosion Resistance Mechanism of Wear Resistance in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.3.3 Surface Chemical Barrier Role in Corrosion Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.4 Analysis of Process-Structure-Property Correlations in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.4.1 Regulatory Role of Sintering Process on Microstructure of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.4.2 Influence Mechanism of Rolling Process on Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.4.3 Optimization Path of Surface Treatment for Chemical Properties of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
4.5 Structure and Property Responses of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Special Environments
4.5.1 Structural Stability Changes of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in High-Temperature Environments
4.5.2 Chemical Structural Tolerance of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Radiation Environments
4.5.3 Property Evolution Laws of Tungsten Alloy Sheets Under Extreme Pressure
4.6 MSDS for CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Sheets
Chapter 5 Performance Testing and Characterization Methods for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.1 Chemical Composition Analysis Techniques for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.1.1 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Emission Spectroscopy Analysis of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.1.2 X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Quantitative Method for Composition of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.1.3 Chemical Titration Analysis of Trace Elements in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.2 Microstructure Characterization Methods for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.2.1 Scanning Electron Microscopy Morphology and Composition Mapping of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.2.2 X-Ray Diffraction Phase and Crystal Structure Analysis of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.2.3 Transmission Electron Microscopy Observation of Microscopic Defects in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.3 Performance Indicator Testing Standards for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.3.1 Testing Methods for Density and Compactness of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.3.2 Testing Methods for Hardness of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.3.3 Testing Methods for Corrosion Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.3.4 Testing Methods for Wear Resistance of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
5.3.5 Testing Methods for Strength of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
Chapter 6 Preparation Processes for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
6.1 Preparation Processes and Classification of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
6.1.1 Main Preparation Routes for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
6.1.2 Process Differences Between High-Density Tungsten Alloy Sheets and Non-High-Density Sheets
6.1.3 Typical Thickness Ranges and Corresponding Process Selection (0.05 mm~50 mm)
6.2 Raw Material Powder Preparation
6.2.1 Preparation and Quality Requirements of High-Purity Tungsten Powder
6.2.2 Selection and Pretreatment of Alloy Element Powders (Ni, Fe, Cu, Co, Mo, etc.)
6.2.3 Powder Particle Size Distribution Control and Fisher Particle Size Testing
6.2.4 Powder Mixing and Alloying Methods
6.3 Powder Forming Processes
6.3.1 Cold Isostatic Pressing
6.3.2 Die Pressing and Pressure Parameter Optimization
6.3.3 Application of Injection Molding in Thin Sheet Blanks
6.3.4 Green Strength Enhancement and Degreasing Processes
6.4 Sintering Processes
6.4.1 Hydrogen Atmosphere Vertical Sintering Technology
6.4.2 Liquid Phase Sintering Temperature Window and Holding Time Control
6.4.3 Vacuum Sintering and Integrated Sintering-Hot Isostatic Pressing Process
6.4.4 Sintering Deformation Control and Support Tooling Design
6.4.5 Temperature Field Uniformity Assurance for Large-Size Plate Blank Sintering
6.5 Hot Working and Heat Treatment
6.5.1 Blooming Forging and Hot Rolling Processes
6.5.2 Multi-Directional Forging to Improve Tissue Uniformity
6.5.3 Intermediate Annealing and Stress Relief Heat Treatment
6.5.4 High-Temperature Solution Treatment and Rapid Cooling
6.6 Cold Rolling and Warm Rolling for Thin Sheet Preparation
6.6.1 Total Deformation Distribution in Cold Rolling and Pass Reduction Schedule
6.6.2 Application of Warm Rolling in High-Tungsten Content Alloys
6.6.3 Rolling Direction Control and Texture Optimization
6.6.4 Edge Crack Prevention and Trimming Processes
6.7 Surface Treatment and Finishing
6.7.1 Chemical Cleaning and Pickling to Remove Oxide Layers
6.7.2 Alkaline Cleaning to Remove Binder Phase Surface Enrichment
6.7.3 Mechanical Grinding and Polishing
6.7.4 Vacuum/Hydrogen Protection Hot Leveling Process
6.7.5 Precision Shearing, Laser Cutting, and Water Jet Cutting
Chapter 7 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
7.1 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in National Defense and Military Fields
7.1.1 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Armor Piercing
7.1.2 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Counterweights
7.1.3 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Protection
7.2 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in High-End Manufacturing Fields
7.2.1 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Mold Inserts
7.2.2 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Cutting Tools
7.2.3 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Mechanical Counterweights
7.3 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Nuclear and Medical Fields
7.3.1 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Nuclear Shielding
7.3.2 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Medical Shielding
7.3.3 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Nuclear Environments
7.4 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Electronics and New Energy Fields
7.4.1 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Heat Dissipation Substrates
7.4.2 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Electronic Packaging
7.4.3 Tungsten Alloy Sheets for Electrodes
7.5 Applications of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Cards
7.5.1 Tungsten Alloy Bank Cards and Payment Cards
7.5.2 Tungsten Alloy Pet Identification Tags
7.5.3 Tungsten Alloy Festival and Commemorative Custom Cards
7.5.4 Tungsten Alloy Industrial and Asset Management Tags
7.5.5 Tungsten Alloy Clothing and Luxury Item Hang Tags
7.5.6 Tungsten Alloy High-End Business Cards and Social Etiquette Cards
Chapter 8 Common Problems and Solutions for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
8.1 Material Foundation Problems and Solutions for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
8.1.1 Composition and Structure-Related Problems
8.1.1.1 Problems of Uneven Composition in Tungsten Alloys and Homogenization Methods
8.1.1.2 Types of Crystal Structure Defects and Repair Strategies
8.1.2 Physical Property Deviation Problems in Tungsten Alloy Sheets
8.1.2.1 Causes and Adjustment Techniques for Abnormal Density and Hardness
8.1.2.2 Problems of Mismatched Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Expansion and Optimization Solutions
8.2 Production and Manufacturing Problems and Solutions for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
8.2.1 Powder Metallurgy Process Problems
8.2.1.1 Identification and Control Measures for Powder Preparation Defects
8.2.1.2 Diagnosis and Process Improvement for Sintering Process Failures
8.2.2 Rolling and Forming Problems
8.2.2.1 Causes and Prevention Methods for Hot Rolling Cracks
8.2.2.2 Analysis and Deformation Control of Cold Working Deformation Problems
8.2.3 Quality Inspection and Control Problems
8.2.3.1 Application Difficulties of Non-Destructive Testing Technology and Alternative Solutions
8.2.3.2 Handling of Dimensional Tolerance Deviations and Precision Improvement
8.3 Application and Performance Problems and Solutions for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
8.3.1 Application Problems of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Aerospace
8.3.1.1 Mechanisms of High-Temperature Fatigue Failure and Strengthening Treatments
8.3.1.2 Problems of Vibration and Impact Loads and Impact-Resistant Design
8.3.2 Application Problems of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Radiation Shielding
8.3.2.1 Causes of Shielding Efficiency Attenuation and Efficiency Recovery
8.3.2.2 Assessment of Biocompatibility Risks and Safety Improvements
8.3.3 Application Problems of Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Electronics and Medical Equipment
8.3.3.1 Troubleshooting of Abnormal Conductivity and Magnetism and Material Modification
8.3.3.2 Protection Against Corrosion and Oxidation Problems and Coating Technology
Appendices:
Appendix A Chinese Standards for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
Appendix B International Standards for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
Appendix C Standards for Tungsten Alloy Sheets in Europe, America, Japan, Korea, and Other Countries
Appendix D Terminology Table for Tungsten Alloy Sheets
References.
Chapter 1: Basic Understanding of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
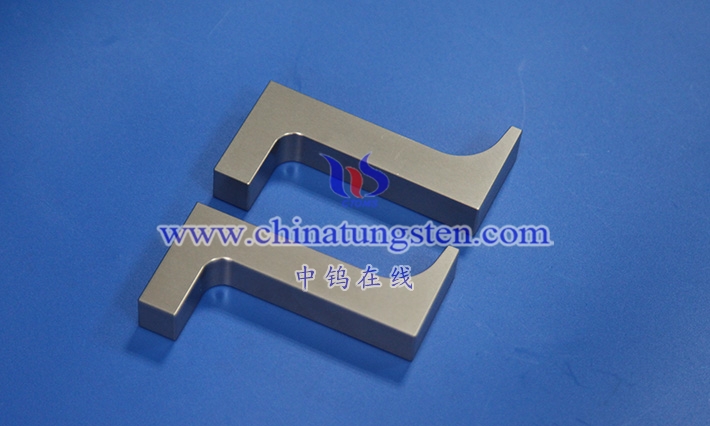
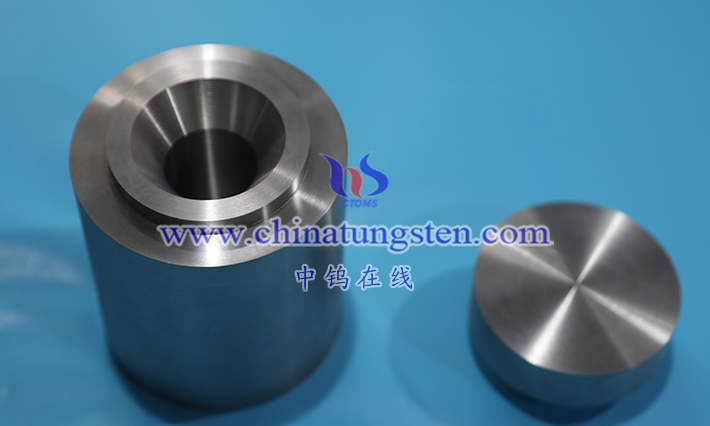
1.1 The concept of tungsten alloy sheets
Tungsten alloy sheets are materials with tungsten as the main component, which are alloyed and processed into thin sheets. This material plays an important role in industrial applications because it combines the high density and high melting point of tungsten with improved processing performance and mechanical behavior through the addition of other elements. The advent of tungsten alloy sheets has enabled tungsten , a metal that was previously difficult to process, to be used in sheet form in various engineering applications.
tungsten alloy sheets typically revolves around a high tungsten content, with other elements chosen to optimize overall performance. Common alloy systems include combinations of tungsten with nickel , iron, or copper, which form a binder phase during sintering, helping the tungsten particles to bond better. The sheet thickness is often controlled to within a few millimeters, or even down to the micrometer level, depending on the specific manufacturing process and application requirements. The production process begins with powder mixing, followed by pressing, sintering, hot working, and cold working, ultimately yielding sheets with smooth surfaces and regular edges.
In terms of performance, tungsten alloy sheets exhibit good density distribution, making them excellent for applications requiring concentrated weight. They also possess a degree of ductility, facilitating subsequent bending, stamping, or cutting operations. The heat treatment process is crucial; by controlling the temperature and cooling rate, the grain size and phase distribution of the material can be adjusted, thereby influencing the balance between hardness and toughness.
Tungsten alloy sheets emphasizes the comprehensive application of materials engineering. It’s not simply about rolling tungsten thinner; rather, it involves alloying to transform brittleness into machinability. This material is gaining acceptance in electronics, medical devices, and precision instruments because it meets requirements for dimensional stability and environmental adaptability. With advancements in manufacturing technologies such as laser cutting and precision rolling, the range of tungsten alloy sheet specifications continues to expand, satisfying diverse design needs.
1.1.1 Definition of Tungsten Alloy Sheets
Tungsten alloy sheets are defined as thin, sheet-like alloy materials made from tungsten as a matrix, with the addition of small amounts of other metallic elements such as nickel, iron, or copper, prepared by powder metallurgy and rolled into shape. Tungsten typically dominates in the composition, giving the material its fundamental properties of high density and high hardness, while the addition of alloying elements significantly improves the material’s plasticity and processing adaptability.
By definition, the key difference between tungsten alloy sheets and other tungsten products lies in their sheet-like shape and alloy composition. During the manufacturing process, tungsten powder is uniformly mixed with other metal powders and then sintered in a liquid phase at high temperature to form a dense microstructure. Subsequently, it is gradually thinned to the desired thickness through multiple rolling passes, accompanied by annealing to release internal stress. This definition reflects the complete transformation chain of the material from powder to finished product.
READ MORE:What Are Tungsten Alloy Sheets
===================================================================
Customized R&D and Production of Tungsten, Molybdenum Products
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD have been working in the tungsten industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization of tungsten and molybdenum products worldwide, which are tungsten and molybdenum design, R&D, production, and overall solution integrators with high visibility and credibility worldwide.
Chinatungsten Online and CTIA GROUP LTD provide products mainly including: tungsten oxide products, such as tungstates such as APT/WO3; tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder; tungsten metal products such as tungsten wire, tungsten ball, tungsten bar, tungsten electrode, etc.; high-density alloy products, such as dart rods, fishing sinkers, automotive tungsten crankshaft counterweights, mobile phones, clocks and watches, tungsten alloy shielding materials for radioactive medical equipment, etc.; tungsten silver and tungsten copper products for electronic appliances. Cemented carbide products include cutting tools such as cutting, grinding, milling, drilling, planing, wear-resistant parts, nozzles, spheres, anti-skid spikes, molds, structural parts, seals, bearings, high-pressure and high-temperature resistant cavities, top hammers, and other standard and customized high-hardness, high-strength, strong acid and alkali resistant high-performance products. Molybdenum products include molybdenum oxide, molybdenum powder, molybdenum and alloy sintering materials, molybdenum crucibles, molybdenum boats, TZM, TZC, molybdenum wires, molybdenum heating belts, molybdenum spouts, molybdenum copper, molybdenum tungsten alloys, molybdenum sputtering targets, sapphire single crystal furnace components, etc.
If you are interested in related products, please contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com|
Tel: +86 592 5129696 / 86 592 5129595